Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents
- PMID: 25993417
- PMCID: PMC6272636
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20058856
Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents
Abstract
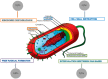
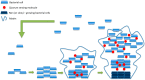
Multi-drug resistance is a growing problem in the treatment of infectious diseases and the widespread use of broad-spectrum antibiotics has produced antibiotic resistance for many human bacterial pathogens. Advances in nanotechnology have opened new horizons in nanomedicine, allowing the synthesis of nanoparticles that can be assembled into complex architectures. Novel studies and technologies are devoted to understanding the mechanisms of disease for the design of new drugs, but unfortunately infectious diseases continue to be a major health burden worldwide. Since ancient times, silver was known for its anti-bacterial effects and for centuries it has been used for prevention and control of disparate infections. Currently nanotechnology and nanomaterials are fully integrated in common applications and objects that we use every day. In addition, the silver nanoparticles are attracting much interest because of their potent antibacterial activity. Many studies have also shown an important activity of silver nanoparticles against bacterial biofilms. This review aims to summarize the emerging efforts to address current challenges and solutions in the treatment of infectious diseases, particularly the use of nanosilver antimicrobials.
Keywords: AgNPs; antibacterial; biofilm; resistence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Seppala H., Klaukka T., Vuopio-Varkila J., Muotiala A., Helenius H., Lager K., Huovinen P. The effect of changes in the consumption of macrolide antibiotics on erythromycin resistance in group A streptococci in Finland. Finnish Study Group for Antimicrobial Resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337:441–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199708143370701. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

