Meta-analysis of Genome-wide Association Studies for Neuroticism, and the Polygenic Association With Major Depressive Disorder
- PMID: 25993607
- PMCID: PMC4667957
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.0554
Meta-analysis of Genome-wide Association Studies for Neuroticism, and the Polygenic Association With Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
Importance: Neuroticism is a pervasive risk factor for psychiatric conditions. It genetically overlaps with major depressive disorder (MDD) and is therefore an important phenotype for psychiatric genetics. The Genetics of Personality Consortium has created a resource for genome-wide association analyses of personality traits in more than 63,000 participants (including MDD cases).
Objectives: To identify genetic variants associated with neuroticism by performing a meta-analysis of genome-wide association results based on 1000 Genomes imputation; to evaluate whether common genetic variants as assessed by single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) explain variation in neuroticism by estimating SNP-based heritability; and to examine whether SNPs that predict neuroticism also predict MDD.
Design, setting, and participants: Genome-wide association meta-analysis of 30 cohorts with genome-wide genotype, personality, and MDD data from the Genetics of Personality Consortium. The study included 63,661 participants from 29 discovery cohorts and 9786 participants from a replication cohort. Participants came from Europe, the United States, or Australia. Analyses were conducted between 2012 and 2014.
Main outcomes and measures: Neuroticism scores harmonized across all 29 discovery cohorts by item response theory analysis, and clinical MDD case-control status in 2 of the cohorts.
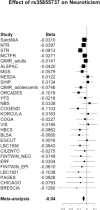
Results: A genome-wide significant SNP was found on 3p14 in MAGI1 (rs35855737; P = 9.26 × 10-9 in the discovery meta-analysis). This association was not replicated (P = .32), but the SNP was still genome-wide significant in the meta-analysis of all 30 cohorts (P = 2.38 × 10-8). Common genetic variants explain 15% of the variance in neuroticism. Polygenic scores based on the meta-analysis of neuroticism in 27 cohorts significantly predicted neuroticism (1.09 × 10-12 < P < .05) and MDD (4.02 × 10-9 < P < .05) in the 2 other cohorts.
Conclusions and relevance: This study identifies a novel locus for neuroticism. The variant is located in a known gene that has been associated with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia in previous studies. In addition, the study shows that neuroticism is influenced by many genetic variants of small effect that are either common or tagged by common variants. These genetic variants also influence MDD. Future studies should confirm the role of the MAGI1 locus for neuroticism and further investigate the association of MAGI1 and the polygenic association to a range of other psychiatric disorders that are phenotypically correlated with neuroticism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Fanous AH, Kendler KS. The genetic relationship of personality to major depression and schizophrenia. Neurotox Res. 2004;6(1):43–50. - PubMed
-
- Kotov R, Gamez W, Schmidt F, Watson D. Linking “Big” Personality Traits to Anxiety, Depressive, and Substance Use Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol Bull. 2010;136(5):768–821. - PubMed
-
- Distel MA, Trull TJ, Willemsen G, et al. The Five Factor Model of personality and borderline personality disorder: A genetic analysis of comorbidity. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:1131–1138. - PubMed
-
- Middeldorp CM, Cath DC, van den Berg M, Beem AL, Van Dyck R, Boomsma DI. The Association of Personality with Anxious and Depressive Psychopathology. In: Canli T, editor. The Biological Basis of Personality and Individual Differences. New York: Guilford Press; 2006. pp. 251–272.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH066206/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA009367/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079469/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA009203/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079470/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA005147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ETM/55/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- RC2 MH089951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/505/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- R01 DA036216/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH046276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 104036/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AA007728/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG006265/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011886/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007580/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007255/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH066140/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZD/16/6/4/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH016880/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA000145/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046289/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA019951/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021336/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AA015416/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA007728/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046318/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA024845/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA002812/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG006265/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013240/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States

