Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Lipo-Dox®) combined with cyclophosphamide and 5-fluorouracil is effective and safe as salvage chemotherapy in taxane-treated metastatic breast cancer: an open-label, multi-center, non-comparative phase II study
- PMID: 25994543
- PMCID: PMC4440506
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1433-4
Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Lipo-Dox®) combined with cyclophosphamide and 5-fluorouracil is effective and safe as salvage chemotherapy in taxane-treated metastatic breast cancer: an open-label, multi-center, non-comparative phase II study
Abstract
Background: Anthracycline and taxane are classes of drugs that are frequently used in the adjuvant and palliative settings of metastatic breast cancer (MBC); however, treatment failure occurs in most cases. Limited data demonstrated favorable response in MBC after previous taxane-based treatment. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Lipo-Dox®) used as part of a combination salvage therapy for patients with MBC whose tumors progressed during or after taxane-based treatment.
Methods: Patients with MBC who failed to respond to previous taxane-based treatments were recruited. Treatment with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (40 mg/m(2)), cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m(2)), and 5-fluorouracil (500 mg/m(2)) was administered every 3 weeks. Tumor response to treatment was determined by using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumor criteria version 1.0, and left ventricular ejection fraction was measured before and after treatment using echocardiography. Each patient was followed for 30 days after the last dose of study medication or until resolution/stabilization of any drug-related adverse event.
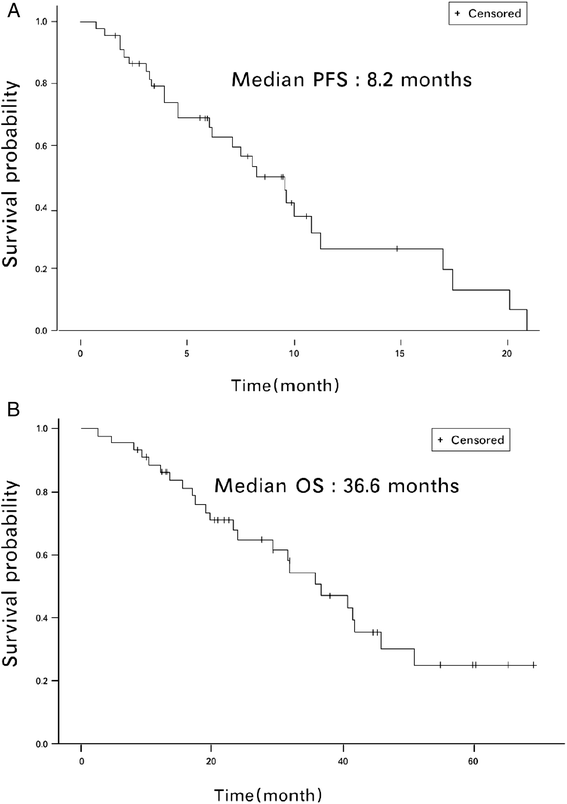
Results: Forty-five patients were recruited. As of December 2012, the median follow-up duration was 29.8 months, the overall response rate was 41.9 %, the median progression-free survival was 8.2 months, and the median overall survival was 36.6 months for all treated patients. Grade 3/4 neutropenia, leucopenia, and neutropenic fever were observed in 14 %, 9 %, and 1 % of the cycles, respectively. Other non-hematologic adverse effects were mild to moderate and were manageable. No decrease in left ventricular ejection function was noted.
Conclusion: This regimen of combined of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and 5-fluorouracil exhibited a promising overall response rate, progression-free survival rate, and overall survival rate, with a safe cardiac toxicity profile and manageable adverse effects. This regimen could be considered as a treatment option for patients with MBC whose tumors progressed during or after taxane-based treatment.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials