Cdc6 degradation requires phosphodegron created by GSK-3 and Cdk1 for SCFCdc4 recognition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 25995377
- PMCID: PMC4501359
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-07-1213
Cdc6 degradation requires phosphodegron created by GSK-3 and Cdk1 for SCFCdc4 recognition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
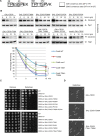
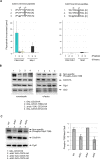
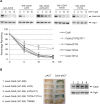
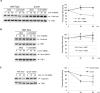
To ensure genome integrity, DNA replication takes place only once per cell cycle and is tightly controlled by cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk1). Cdc6p is part of the prereplicative complex, which is essential for DNA replication. Cdc6 is phosphorylated by cyclin-Cdk1 to promote its degradation after origin firing to prevent DNA rereplication. We previously showed that a yeast GSK-3 homologue, Mck1 kinase, promotes Cdc6 degradation in a SCF(Cdc4)-dependent manner, therefore preventing rereplication. Here we present evidence that Mck1 directly phosphorylates a GSK-3 consensus site in the C-terminus of Cdc6. The Mck1-dependent Cdc6 phosphorylation required priming by cyclin/Cdk1 at an adjacent CDK consensus site. The sequential phosphorylation by Mck1 and Clb2/Cdk1 generated a Cdc4 E3 ubiquitin ligase-binding motif to promote Cdc6 degradation during mitosis. We further revealed that Cdc6 degradation triggered by Mck1 kinase was enhanced upon DNA damage caused by the alkylating agent methyl methanesulfonate and that the resulting degradation was mediated through Cdc4. Thus, Mck1 kinase ensures proper DNA replication, prevents DNA damage, and maintains genome integrity by inhibiting Cdc6.
© 2015 Al-Zain et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures
Similar articles
-
A yeast GSK-3 kinase Mck1 promotes Cdc6 degradation to inhibit DNA re-replication.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(12):e1003099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003099. Epub 2012 Dec 6. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23236290 Free PMC article.
-
Mck1-mediated proteolysis of CENP-A prevents mislocalization of CENP-A for chromosomal stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2024 Sep 4;228(1):iyae108. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae108. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38984710 Free PMC article.
-
Separate SCF(CDC4) recognition elements target Cdc6 for proteolysis in S phase and mitosis.EMBO J. 2001 Sep 3;20(17):4836-45. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4836. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11532947 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc6 and DNA replication: limited to humble origins.Bioessays. 1996 Nov;18(11):859-62. doi: 10.1002/bies.950181103. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8939063 Review.
-
[Involvement of cyclin-dependent kinase CDK1/CDC28 in regulation of cell cycle].Genetika. 2013 Jul;49(7):797-813. doi: 10.7868/s0016675813050093. Genetika. 2013. PMID: 24450149 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The Yeast Gsk-3 Kinase Mck1 Is Necessary for Cell Wall Remodeling in Glucose-Starved and Cell Wall-Stressed Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 9;26(8):3534. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083534. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332024 Free PMC article.
-
The CWI Pathway: A Versatile Toolbox to Arrest Cell-Cycle Progression.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Dec 4;7(12):1041. doi: 10.3390/jof7121041. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-cycle phospho-regulation of the kinetochore.Curr Genet. 2021 Apr;67(2):177-193. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01127-2. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33221975 Review.
-
The interplay between cell wall integrity and cell cycle progression in plants.Plant Mol Biol. 2023 Dec;113(6):367-382. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01394-w. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Plant Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38091166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Model Explaining the Role of CDC6 in the Diauxic Growth of CDK1 Activity during the M-Phase of the Cell Cycle.Cells. 2019 Nov 28;8(12):1537. doi: 10.3390/cells8121537. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31795221 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

