Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin functionalized calcium carbonate microparticles as a potential carrier for enhancing oral delivery of water-insoluble drugs
- PMID: 25995635
- PMCID: PMC4425320
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S78814
Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin functionalized calcium carbonate microparticles as a potential carrier for enhancing oral delivery of water-insoluble drugs
Abstract
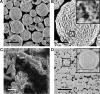
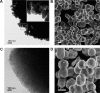
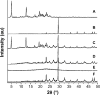
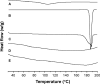
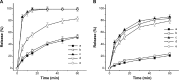
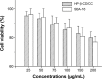
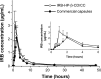
The objective of the present study was to demonstrate that a novel hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin functionalized calcium carbonate (HP-β-CD/CC) based amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) can be used to increase the solubility and oral bioavailability of water-insoluble drugs. Irbesartan (IRB) was selected as a model compound and loaded into the nanoporous HP-β-CD/CC matrix using an immersion method. The IRB-loaded HP-β-CD/CC formulation was characterized by various analytical techniques, such as specific surface area analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Analyses with PXRD and DSC confirmed that IRB was fully converted into the amorphous form in the nanopores of HP-β-CD/CC. From the solubility and dissolution tests, it was observed that the aqueous solubility and dissolution rate of IRB-loaded HP-β-CD/CC were increased significantly compared with those of pure IRB and IRB-loaded mesoporous silica. Likewise, the IRB-loaded HP-β-CD/CC formulation exhibited better absorption compared with that of the commercially available IRB capsules in beagle dogs. The mean peak plasma concentration (C max) and the area under the mean plasma concentration-time curve (AUC[0→48]) of IRB-loaded HP-β-CD/CC were 1.56- and 1.52-fold higher than that of the commercial product, respectively. Furthermore, the IRB-loaded HP-β-CD/CC formulation exhibited excellent stability against re-crystallization. These results clearly demonstrate that HP-β-CD/CC based porous ASD is a promising formulation approach to improve the aqueous solubility and the in vivo absorption performance of a water-insoluble compound like IRB.
Keywords: bioavailability; dissolution rate; nanopore; solid dispersion; solubility.
Figures
References
-
- Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46:3–26. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Parikh T, Sandhu HK, et al. Supersolubilization and amorphization of a model basic drug, haloperidol, by interaction with weak acids. Pharm Res. 2013;30:1561–1573. - PubMed
-
- Brough C, Williams RO. Amorphous solid dispersions and nano-crystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2013;453:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Kawabata Y, Wada K, Nakatani M, Yamada S, Onoue S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: basic approaches and practical applications. Int J Pharm. 2011;420:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Müller RH, Jacobs C, Kayser O. Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy: rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;47:3–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

