MRI features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to biologic behavior
- PMID: 25995679
- PMCID: PMC4435980
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.449
MRI features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to biologic behavior
Abstract
Imaging studies including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play a crucial role in the diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several recent studies reveal a large number of MRI features related to the prognosis of HCC. In this review, we discuss various MRI features of HCC and their implications for the diagnosis and prognosis as imaging biomarkers. As a whole, the favorable MRI findings of HCC are small size, encapsulation, intralesional fat, high apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value, and smooth margins or hyperintensity on the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Unfavorable findings include large size, multifocality, low ADC value, non-smooth margins or hypointensity on hepatobiliary phase images. MRI findings are potential imaging biomarkers in patients with HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prognosis.
Figures
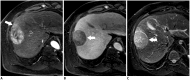


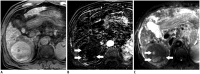



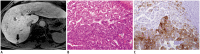
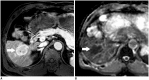
References
-
- Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:519–524. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:225–235. - PubMed
-
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69:89–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

