Quantitative Assessment of Global and Regional Air Trappings Using Non-Rigid Registration and Regional Specific Volume Change of Inspiratory/Expiratory CT Scans: Studies on Healthy Volunteers and Asthmatics
- PMID: 25995694
- PMCID: PMC4435244
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.632
Quantitative Assessment of Global and Regional Air Trappings Using Non-Rigid Registration and Regional Specific Volume Change of Inspiratory/Expiratory CT Scans: Studies on Healthy Volunteers and Asthmatics
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare air trapping in healthy volunteers with asthmatics using pulmonary function test and quantitative data, such as specific volume change from paired inspiratory CT and registered expiratory CT.
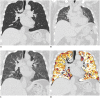
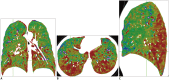
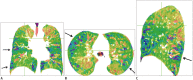
Materials and methods: Sixteen healthy volunteers and 9 asthmatics underwent paired inspiratory/expiratory CT. ΔSV, which represents the ratio of air fraction released after exhalation, was measured with paired inspiratory and anatomically registered expiratory CT scans. Air trapping indexes, ΔSV0.4 and ΔSV0.5, were defined as volume fraction of lung below 0.4 and 0.5 ΔSV, respectively. To assess the gravity effect of air-trapping, ΔSV values of anterior and posterior lung at three different levels were measured and ΔSV ratio of anterior lung to posterior lung was calculated. Color-coded ΔSV map of the whole lung was generated and visually assessed. Mean ΔSV, ΔSV0.4, and ΔSV0.5 were compared between healthy volunteers and asthmatics. In asthmatics, correlation between air trapping indexes and clinical parameters were assessed.
Results: Mean ΔSV, ΔSV0.4, and ΔSV0.5 in asthmatics were significantly higher than those in healthy volunteer group (all p < 0.05). ΔSV values in posterior lung in asthmatics were significantly higher than those in healthy volunteer group (p = 0.049). In asthmatics, air trapping indexes, such as ΔSV0.5 and ΔSV0.4, showed negative strong correlation with FEF25-75, FEV1, and FEV1/FVC. ΔSV map of asthmatics showed abnormal geographic pattern in 5 patients (55.6%) and disappearance of anterior-posterior gradient in 3 patients (33.3%).
Conclusion: Quantitative assessment of ΔSV (the ratio of air fraction released after exhalation) shows the difference in extent of air trapping between health volunteers and asthmatics.
Keywords: Air trapping; Asthma; Quantitative assessment; Registration; Specific volume change.
Figures
References
-
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(5 Suppl):S94–S138. - PubMed
-
- Grant EN, Wagner R, Weiss KB. Observations on emerging patterns of asthma in our society. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104(2 Pt 2):S1–S9. - PubMed
-
- Anandan C, Nurmatov U, van Schayck OC, Sheikh A. Is the prevalence of asthma declining? Systematic review of epidemiological studies. Allergy. 2010;65:152–167. - PubMed
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Bailey C, Zahran HS, King M, Johnson CA, et al. Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001-2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012;(94):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Austin JH, Müller NL, Friedman PJ, Hansell DM, Naidich DP, Remy-Jardin M, et al. Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 1996;200:327–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

