Women with large (≥3 cm) and locally advanced breast cancers (T3, 4, N1, 2, M0) receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC: cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, docetaxel): addition of capecitabine improves 4-year disease-free survival
- PMID: 25995984
- PMCID: PMC4429427
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-4-9
Women with large (≥3 cm) and locally advanced breast cancers (T3, 4, N1, 2, M0) receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC: cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, docetaxel): addition of capecitabine improves 4-year disease-free survival
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether capecitabine (X), combined with docetaxel (T) following doxorubicin (A) and cyclophosphamide (C), enhanced the pathological complete response (pCR) in the breast and axillary lymph nodes (ALNs) of women with large or locally advanced breast cancers (LLABCs) improving outcome, and the effect on quality of life (QoL).
Patients and methods: 117 women were enrolled, 112 randomised to 2 cycles of AC (60 mg/m(2), 600 mg/m(2)) given 3 weekly. Tumour responses were assessed by magnetic resonance mammography. Responders (n = 77) received 2 further cycles of AC and were randomised to 4 cycles of T (100 mg/m(2)) (Group A) or T (75 mg/m(2)) and X (2000 mg/m(2)/day), day one to 14 of each 3 weekly cycle (Group B). Non-responders (n = 35) were randomised to 6 cycles of T (Group C) or T + X (Group D). QoL questionnaires were completed at each chemotherapy visit. Pathological responses were evaluated using established criteria.
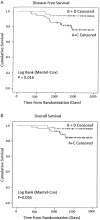
Results: The groups were comparable in patient and tumour characteristics (79.5% T2, 85.7% ductal, 73.2% ER +ve, 22.3% HER2 +ve, 42% involved ALNs). Overall breast pCR was 27.1%, Groups A + C versus B + D (p = 0.446). ALN +ve pCR was 41.9%, Groups A + C versus B + D (p = 0.231). 4-year disease-free survival (DFS) was significantly improved with X (p = 0.016) but not overall survival (p = 0.056). Triple -ve and HER2 +ve tumours, and persistent ALN disease were risk factors for metastases. X increased severe nail changes (p = 0.0002) and hand-foot syndrome (p = 0.014) without affecting QoL.
Conclusion: NAC-X did not increase breast and ALN pCR but improved 4-year DFS, without detriment to QoL.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Response; Survival.
Figures
References
-
- Bear HD, Anderson S, Smith RE, Geyer CE, Jr, Mamounas EP, Fisher B, Brown AM, Robidoux A, Margolese R, Kahlenberg MS, Paik S, Soran A, Wickerham DL, Wolmark N. Sequential preoperative or postoperative docetaxel added to preoperative doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide for operable breast cancer: national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(13):2019–2027. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.1665. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bear HD, Tang G, Rastogi P, Geyer CE, Jr, Robidoux A, Atkins JN, Baez-Diaz L, Brufsky AM, Mehta RS, Fehrenbacher L, Young JA, Senecal FM, Gaur R, Margolese RG, Adams PT, Gross HM, Costantino JP, Swain SM, Mamounas EP, Wolmark N. Bevacizumab added to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(4):310–320. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1111097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brady MJ, Cella DF, Mo F, Bonomi AE, Tulsky DS, Lloyd SR, Deasy S, Cobleigh M, Shiomoto G. Reliability and validity of the functional assessment of cancer therapy-breast quality-of-life instrument. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(3):974–986. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous