Population pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of vedolizumab in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
- PMID: 25996351
- PMCID: PMC5032981
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.13243
Population pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of vedolizumab in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Nov;42(9):1135. doi: 10.1111/apt.13365. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26427757 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Vedolizumab, an anti-α(4)β(7) integrin monoclonal antibody (mAb), is indicated for treating patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). As higher therapeutic mAb concentrations have been associated with greater efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease, understanding determinants of vedolizumab clearance may help to optimise dosing.
Aims: To characterise vedolizumab pharmacokinetics in patients with UC and CD, to identify clinically relevant determinants of vedolizumab clearance, and to describe the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship using population modelling.
Methods: Data from a phase 1 healthy volunteer study, a phase 2 UC study, and 3 phase 3 UC/CD studies were included. Population pharmacokinetic analysis for repeated measures was conducted using nonlinear mixed effects modelling. Results from the base model, developed using extensive phase 1 and 2 data, were used to develop the full covariate model, which was fit to sparse phase 3 data.
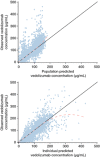
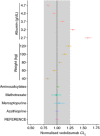
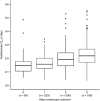
Results: Vedolizumab pharmacokinetics was described by a 2-compartment model with parallel linear and nonlinear elimination. Using reference covariate values, linear elimination half-life of vedolizumab was 25.5 days; linear clearance (CL(L)) was 0.159 L/day for UC and 0.155 L/day for CD; central compartment volume of distribution (V(c)) was 3.19 L; and peripheral compartment volume of distribution was 1.66 L. Interindividual variabilities (%CV) were 35% for CLL and 19% for V(c); residual variance was 24%. Only extreme albumin and body weight values were identified as potential clinically important predictors of CL(L).
Conclusions: Population pharmacokinetic parameters were similar in patients with moderately to severely active UC and CD. This analysis supports use of vedolizumab fixed dosing in these patients. Clinicaltrials.gov Identifiers: NCT01177228; NCT00783718 (GEMINI 1); NCT00783692 (GEMINI 2); NCT01224171 (GEMINI 3).
© 2015 Takeda Pharmaceuticals International Co published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Soler D, Chapman T, Yang LL, Wyant T, Egan R, Fedyk ER. The binding specificity and selective antagonism of vedolizumab, an anti‐alpha4beta7 integrin therapeutic antibody in development for inflammatory bowel diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2009; 330: 864–75. - PubMed
-
- Paul S, Moreau AC, Del Tedesco E, et al Pharmacokinetics of adalimumab in inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 1288–95. - PubMed
-
- Ordas I, Mould DR, Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ. Anti‐TNF Monoclonal Antibodies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pharmacokinetics‐Based Dosing Paradigms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2012; 91: 635–46. - PubMed
-
- Colombel JF, Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Van Assche G, Robinson AM. Therapeutic drug monitoring of biologics for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2012a; 18: 349–58. - PubMed
-
- Feagan BG, Greenberg GR, Wild G, et al Treatment of active Crohn's disease with MLN0002, a humanized antibody to the alpha4beta7 integrin. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 6: 1370–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
