Cloning and characterization of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase from the highly branched isoprenoid producing diatom Rhizosolenia setigera
- PMID: 25996801
- PMCID: PMC4440519
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10246
Cloning and characterization of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase from the highly branched isoprenoid producing diatom Rhizosolenia setigera
Abstract
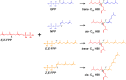
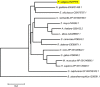
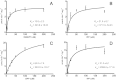
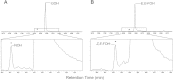
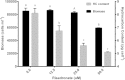
The diatom Rhizosolenia setigera Brightwell produces highly branched isoprenoid (HBI) hydrocarbons that are ubiquitously present in marine environments. The hydrocarbon composition of R. setigera varies between C25 and C30 HBIs depending on the life cycle stage with regard to auxosporulation. To better understand how these hydrocarbons are biosynthesized, we characterized the farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) synthase (FPPS) enzyme of R. setigera. An isolated 1465-bp cDNA clone contained an open reading frame spanning 1299-bp encoding a protein with 432 amino acid residues. Expression of the RsFPPS cDNA coding region in Escherichia coli produced a protein that exhibited FPPS activity in vitro. A reduction in HBI content from diatoms treated with an FPPS inhibitor, risedronate, suggested that RsFPPS supplies precursors for HBI biosynthesis. Product analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry also revealed that RsFPPS produced small amounts of the cis-isomers of geranyl pyrophosphate and FPP, candidate precursors for the cis-isomers of HBIs previously characterized. Furthermore, RsFPPS gene expression at various life stages of R. setigera in relation to auxosporulation were also analyzed. Herein, we present data on the possible role of RsFPPS in HBI biosynthesis, and it is to our knowledge the first instance that an FPPS was cloned and characterized from a diatom.
Figures

References
-
- Mann D. G. & Vanormelingen P. An inordinate fondness? The number, distributions, and origins of diatom species. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 60, 414–420 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Gao K. et al. Rising CO2 and increased light exposure synergistically reduce marine primary productivity. Nature Clim. Change 2, 519–523 (2012).
-
- Sinninghe Damste J. S. et al. The rise of rhizosolenid diatoms. Science 304, 584–587 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Rowland S. J. & Robson J. N. The widespread occurrence of highly branched acyclic C20, C25 and C30 hydrocarbons in recent sediments and biota - A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 30, 191–216 (1990).
-
- Rowland S. J., Belt S. T., Masse G., Roussakis C. & Robert J.-M. Effects of temperature on polyunsaturation in cytostatic lipids of Haslea ostrearia. Phytochemistry 56, 597–602 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

