A Highly Efficient Gene Expression Programming (GEP) Model for Auxiliary Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 25996920
- PMCID: PMC4440826
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125517
A Highly Efficient Gene Expression Programming (GEP) Model for Auxiliary Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is an important and common cancer that constitutes a major public health problem, but early detection of small cell lung cancer can significantly improve the survival rate of cancer patients. A number of serum biomarkers have been used in the diagnosis of lung cancers; however, they exhibit low sensitivity and specificity.
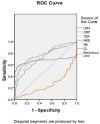
Methods: We used biochemical methods to measure blood levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), C-reactive protein (CRP), Na+, Cl-, carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA), and neuron specific enolase (NSE) in 145 small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients and 155 non-small cell lung cancer and 155 normal controls. A gene expression programming (GEP) model and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves incorporating these biomarkers was developed for the auxiliary diagnosis of SCLC.
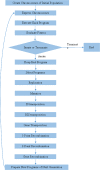
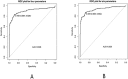
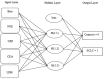
Results: After appropriate modification of the parameters, the GEP model was initially set up based on a training set of 115 SCLC patients and 125 normal controls for GEP model generation. Then the GEP was applied to the remaining 60 subjects (the test set) for model validation. GEP successfully discriminated 281 out of 300 cases, showing a correct classification rate for lung cancer patients of 93.75% (225/240) and 93.33% (56/60) for the training and test sets, respectively. Another GEP model incorporating four biomarkers, including CEA, NSE, LDH, and CRP, exhibited slightly lower detection sensitivity than the GEP model, including six biomarkers. We repeat the models on artificial neural network (ANN), and our results showed that the accuracy of GEP models were higher than that in ANN. GEP model incorporating six serum biomarkers performed by NSCLC patients and normal controls showed low accuracy than SCLC patients and was enough to prove that the GEP model is suitable for the SCLC patients.
Conclusion: We have developed a GEP model with high sensitivity and specificity for the auxiliary diagnosis of SCLC. This GEP model has the potential for the wide use for detection of SCLC in less developed regions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of lung cancer based on serum biomarkers by gene expression programming methods.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(21):9367-73. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.21.9367. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25422226
-
Diagnostic potential of protein serum biomarkers for distinguishing small and non-small cell lung cancer in patients with suspicious lung lesions.Biomarkers. 2024 Jul;29(5):315-323. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2024.2360038. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Biomarkers. 2024. PMID: 38804910
-
Application of Serum ELAVL4 (HuD) Antigen Assay for Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis.Anticancer Res. 2017 Aug;37(8):4515-4522. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11848. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28739747
-
High Serum Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE) Level Firstly Ignored as Normal Reaction in a Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient: a Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Lab. 2019 Jan 1;65(1). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180703. Clin Lab. 2019. PMID: 30775876 Review.
-
Will liquid biopsies improve outcomes for patients with small-cell lung cancer?Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):e470-e481. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30455-8. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30191851 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a Diagnostic Model for Small Cell Lung Cancer Combining Metabolomics and Integrated Machine Learning.Oncologist. 2024 Mar 4;29(3):e392-e401. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad261. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37706531 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the use of artificial neural networks in lung cancer research.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Apr;9(4):924-931. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.03.157. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 28523139 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Neural Networks in Lung Cancer Research: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 22;12(3):880. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030880. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Stacking Machine Learning Model for Small Cell Lung Cancer Prediction Using Metabolomics Profiling.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;16(24):4225. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244225. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766124 Free PMC article.
-
A novel gene selection algorithm for cancer classification using microarray datasets.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Jan 15;12(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0447-6. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30646919 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

