Feeding and Fasting Signals Converge on the LKB1-SIK3 Pathway to Regulate Lipid Metabolism in Drosophila
- PMID: 25996931
- PMCID: PMC4440640
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005263
Feeding and Fasting Signals Converge on the LKB1-SIK3 Pathway to Regulate Lipid Metabolism in Drosophila
Abstract
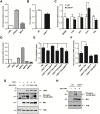
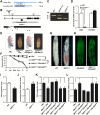
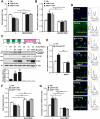
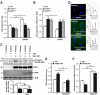
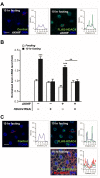
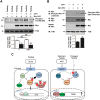
LKB1 plays important roles in governing energy homeostasis by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and other AMPK-related kinases, including the salt-inducible kinases (SIKs). However, the roles and regulation of LKB1 in lipid metabolism are poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila LKB1 mutants display decreased lipid storage and increased gene expression of brummer, the Drosophila homolog of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). These phenotypes are consistent with those of SIK3 mutants and are rescued by expression of constitutively active SIK3 in the fat body, suggesting that SIK3 is a key downstream kinase of LKB1. Using genetic and biochemical analyses, we identify HDAC4, a class IIa histone deacetylase, as a lipolytic target of the LKB1-SIK3 pathway. Interestingly, we found that the LKB1-SIK3-HDAC4 signaling axis is modulated by dietary conditions. In short-term fasting, the adipokinetic hormone (AKH) pathway, related to the mammalian glucagon pathway, inhibits the kinase activity of LKB1 as shown by decreased SIK3 Thr196 phosphorylation, and consequently induces HDAC4 nuclear localization and brummer gene expression. However, under prolonged fasting conditions, AKH-independent signaling decreases the activity of the LKB1-SIK3 pathway to induce lipolytic responses. We also identify that the Drosophila insulin-like peptides (DILPs) pathway, related to mammalian insulin pathway, regulates SIK3 activity in feeding conditions independently of increasing LKB1 kinase activity. Overall, these data suggest that fasting stimuli specifically control the kinase activity of LKB1 and establish the LKB1-SIK3 pathway as a converging point between feeding and fasting signals to control lipid homeostasis in Drosophila.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A hormone-dependent module regulating energy balance.Cell. 2011 May 13;145(4):596-606. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.013. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21565616 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor kinase LKB1 activates the downstream kinases SIK2 and SIK3 to stimulate nuclear export of class IIa histone deacetylases.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 29;288(13):9345-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.456996. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23393134 Free PMC article.
-
SIK3-HDAC4 signaling regulates Drosophila circadian male sex drive rhythm via modulating the DN1 clock neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 8;114(32):E6669-E6677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620483114. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28743754 Free PMC article.
-
AMPKα-like proteins as LKB1 downstream targets in cell physiology and cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 May;99(5):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02040-y. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33661342 Review.
-
The Salt-Inducible Kinases: Emerging Metabolic Regulators.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Dec;29(12):827-840. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30385008 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila as a Model to Study the Link between Metabolism and Cancer.J Dev Biol. 2017 Dec 1;5(4):15. doi: 10.3390/jdb5040015. J Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 29615570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sugar-responsive enteroendocrine neuropeptide F regulates lipid metabolism through glucagon-like and insulin-like hormones in Drosophila melanogaster.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 10;12(1):4818. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25146-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34376687 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic rate and hypoxia tolerance are affected by group interactions and sex in the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster): new data and a literature survey.Biol Open. 2017 Apr 15;6(4):471-480. doi: 10.1242/bio.023994. Biol Open. 2017. PMID: 28202465 Free PMC article.
-
BubR1 controls starvation-induced lipolysis via IMD signaling pathway in Drosophila.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 8;16(4):3257-3279. doi: 10.18632/aging.205533. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38334966 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Characterization of Hermetia illucens Larval Midgut.Front Physiol. 2019 Mar 8;10:204. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00204. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30906266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kopelman PG (2000) Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404: 635–643. - PubMed
-
- Gronke S, Mildner A, Fellert S, Tennagels N, Petry S, et al. (2005) Brummer lipase is an evolutionary conserved fat storage regulator in Drosophila. Cell Metab 1: 323–330. - PubMed
-
- Kim SK, Rulifson EJ (2004) Conserved mechanisms of glucose sensing and regulation by Drosophila corpora cardiaca cells. Nature 431: 316–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

