DA-Raf-Mediated Suppression of the Ras--ERK Pathway Is Essential for TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cells
- PMID: 25996975
- PMCID: PMC4440819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127888
DA-Raf-Mediated Suppression of the Ras--ERK Pathway Is Essential for TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cells
Abstract
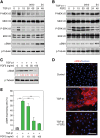
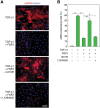
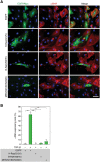
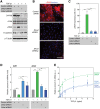
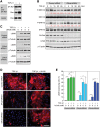
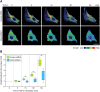
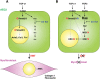
Myofibroblasts play critical roles in the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by depositing components of extracellular matrix. One source of lung myofibroblasts is thought to be alveolar epithelial type 2 cells that undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Rat RLE-6TN alveolar epithelial type 2 cells treated with transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) are converted into myofibroblasts through EMT. TGF-β induces both canonical Smad signaling and non-canonical signaling, including the Ras-induced ERK pathway (Raf-MEK-ERK). However, the signaling mechanisms regulating TGF-β1-induced EMT are not fully understood. Here, we show that the Ras-ERK pathway negatively regulates TGF-β1-induced EMT in RLE-6TN cells and that DA-Raf1 (DA-Raf), a splicing isoform of A-Raf and a dominant-negative antagonist of the Ras-ERK pathway, plays an essential role in EMT. Stimulation of the cells with fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), which activated the ERK pathway, prominently suppressed TGF-β1-induced EMT. An inhibitor of MEK, but not an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, rescued the TGF-β1-treated cells from the suppression of EMT by FGF2. Overexpression of a constitutively active mutant of a component of the Ras-ERK pathway, i.e., H-Ras, B-Raf, or MEK1, interfered with EMT. Knockdown of DA-Raf expression with siRNAs facilitated the activity of MEK and ERK, which were only weakly and transiently activated by TGF-β1. Although DA-Raf knockdown abrogated TGF-β1-induced EMT, the abrogation of EMT was reversed by the addition of the MEK inhibitor. Furthermore, DA-Raf knockdown impaired the TGF-β1-induced nuclear translocation of Smad2, which mediates the transcription required for EMT. These results imply that intrinsic DA-Raf exerts essential functions for EMT by antagonizing the TGF-β1-induced Ras-ERK pathway in RLE-6TN cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRPC1/3/6 inhibition attenuates the TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer via the Ras/Raf1/ERK signaling pathway.Cell Biol Int. 2018 Aug;42(8):975-984. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10963. Epub 2018 May 10. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 29570903
-
The effect of TGF-β1 and Smad7 gene transfer on the phenotypic changes of rat alveolar epithelial cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2007 Sep;12(3):457-72. doi: 10.2478/s11658-007-0018-x. Epub 2007 Apr 24. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17457524 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Impact and Mechanism on Broncho-Pulmonary Dysplasia.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025;186(8):769-783. doi: 10.1159/000543105. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39694023
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
-
Dominant-negative antagonists of the Ras-ERK pathway: DA-Raf and its related proteins generated by alternative splicing of Raf.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Feb 15;387(2):111775. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111775. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31843497 Review.
Cited by
-
Telomerase Deficiency Causes Alveolar Stem Cell Senescence-associated Low-grade Inflammation in Lungs.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 25;290(52):30813-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.681619. Epub 2015 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26518879 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain 1 regulates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lung epithelial cells via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Mar 15;9(3):1402-1409. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28386365 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the pharmacological mechanism of Yifei Tongluo granules in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jun 2;102(22):e33729. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033729. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37266620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote lung cancer metastasis by CCL11 to activate ERK and AKT signaling and induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor cells.Oncogene. 2021 Feb;40(8):1476-1489. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01605-4. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33452453
-
IL-27 induces autophagy through regulation of the DNMT1/lncRNA MEG3/ERK/p38 axis to reduce pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2023 Mar 3;24(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02373-x. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 36869378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thannickal VJ, Toews GB, White ES, Lynch JP III, Martinez FJ (2004) Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Med 55: 395–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

