Inhibition of hTERT/telomerase contributes to the antitumor activity of pristimerin in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 25997419
- PMCID: PMC4484616
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2015.3989
Inhibition of hTERT/telomerase contributes to the antitumor activity of pristimerin in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells
Abstract
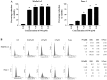
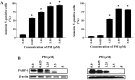
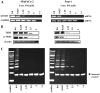
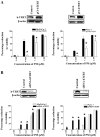
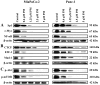
Pristimerin (PM) is a promising anticancer agent that has exhibited strong antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity in various types of cancer cells. In the present study, we investigated the role of telomerase in mediating the antitumor activity of PM in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) cells. PM inhibited cell proliferation, arrested cells in the G1 cell cycle phase and induced apoptosis in MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 PDA cells. These antitumor activities of PM correlated well with the inhibition of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT), the gene that codes for the catalytic subunit of telomerase complex. Gene knockin and knockdown approaches demonstrated that hTERT regulates the response of PDA cells to PM. PM inhibited hTERT expression by suppressing the transcription factors Sp1, c-Myc and NF-κB which control hTERT gene expression. PM also inhibited protein kinase Akt, which phosphorylates and facilitates hTERT nuclear importation and its telomerase activity. These findings identified hTERT (telomerase) as a potential therapeutic target of PM for the treatment of PDA.
Figures
References
-
- Pancreatic Cancer-National Cancer Institute, U.S. National Institutes of Health Cancer Gov. http:www.cancer.gov/cancer-topics/types/pancreatic. Retrieved 06-04-2010.
-
- Mulcahy MF, Wahl AO, Small W., Jr The current status of combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced or resected pancreas cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2005;3:637–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

