Methodology and effects of repeated intranasal delivery of DNSP-11 in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 25999268
- PMCID: PMC4500736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.05.006
Methodology and effects of repeated intranasal delivery of DNSP-11 in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: To circumvent the challenges associated with delivering large compounds directly to the brain for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD), non-invasive procedures utilizing smaller molecules with protective and/or restorative actions on dopaminergic neurons are needed.
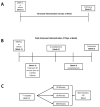
New method: We developed a methodology for evaluating the effects of a synthetic neuroactive peptide, DNSP-11, on the nigrostriatal system using repeated intranasal delivery in both normal and a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesion rat model of PD.
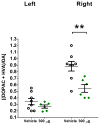
Results: Normal rats repeatedly administered varying doses of DNSP-11 intranasally for 3 weeks exhibited a significant increase in dopamine (DA) turnover in both the striatum and substantia nigra (SN) at 300μg, suggestive of a stimulative effect of the dopaminergic system. Additionally, a protective effect was observed following repeated intranasal administration in 6-OHDA lesioned rats, as suggested by: a significant decrease in d-amphetamine-induced rotation at 2 weeks; a decrease in DA turnover in the lesioned striatum; and an increased sparing of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive (+) neurons in a specific sub-region of the lesioned substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Finally, tracer studies showed (125)I-DNSP-11 distributed diffusely throughout the brain, including the striatum and SN, as quickly as 30min after a single intranasal dose.
Comparison with existing methods: The results of bilateral intranasal administration of DNSP-11 are compared to our unilateral single infusion studies to the brain in rats.
Conclusions: These studies support that DNSP-11 can be delivered intranasally and maintain its neuroactive properties in both normal rats and in a unilateral 6-OHDA rat model of PD.
Keywords: 6-Hydroxydopamine; Intranasal administration; Neurochemistry; Neuroprotection; Nigrostriatal pathway; Peptide.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


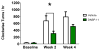



References
-
- Gash DM, et al. Functional recovery in parkinsonian monkeys treated with GDNF. Nature. 1996;380(6571):252–255. - PubMed
-
- Lin L, et al. GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science. 1993;260(5111):1130–1132. - PubMed
-
- Gill SS, et al. Direct brain infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 2003;9(5):589–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016481/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS060924/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS060924/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR033173/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS075694/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039787/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS039787/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000242/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS075694/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033173/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103436/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P20 GM103436-12/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P20RR016481-12/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG013494/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AG000242/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG013494/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

