Primerize: automated primer assembly for transcribing non-coding RNA domains
- PMID: 25999345
- PMCID: PMC4489279
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv538
Primerize: automated primer assembly for transcribing non-coding RNA domains
Abstract
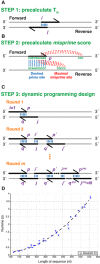
Customized RNA synthesis is in demand for biological and biotechnological research. While chemical synthesis and gel or chromatographic purification of RNA is costly and difficult for sequences longer than tens of nucleotides, a pipeline of primer assembly of DNA templates, in vitro transcription by T7 RNA polymerase and kit-based purification provides a cost-effective and fast alternative for preparing RNA molecules. Nevertheless, designing template primers that optimize cost and avoid mispriming during polymerase chain reaction currently requires expert inspection, downloading specialized software or both. Online servers are currently not available or maintained for the task. We report here a server named Primerize that makes available an efficient algorithm for primer design developed and experimentally tested in our laboratory for RNA domains with lengths up to 300 nucleotides. Free access: http://primerize.stanford.edu.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Qi L.S., Arkin A.P. A versatile framework for microbial engineering using synthetic non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2014;12:341–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

