Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies
- PMID: 25999452
- PMCID: PMC4490298
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-580027
Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies
Abstract
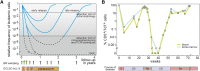
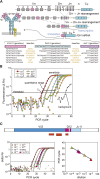
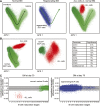
Monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD) has become routine clinical practice in frontline treatment of virtually all childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and in many adult ALL patients. MRD diagnostics has proven to be the strongest prognostic factor, allowing for risk group assignment into different treatment arms, ranging from significant treatment reduction to mild or strong intensification. Also in relapsed ALL patients and patients undergoing stem cell transplantation, MRD diagnostics is guiding treatment decisions. This is also why the efficacy of innovative drugs, such as antibodies and small molecules, are currently being evaluated with MRD diagnostics within clinical trials. In fact, MRD measurements might well be used as a surrogate end point, thereby significantly shortening the follow-up. The MRD techniques need to be sensitive (≤10(-4)), broadly applicable, accurate, reliable, fast, and affordable. Thus far, flow cytometry and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of rearranged immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes (allele-specific oligonucleotide [ASO]-PCR) are claimed to meet these criteria, but classical flow cytometry does not reach a solid 10(-4), whereas classical ASO-PCR is time-consuming and labor intensive. Therefore, 2 high-throughput technologies are being explored, ie, high-throughput sequencing and next-generation (multidimensional) flow cytometry, both evaluating millions of sequences or cells, respectively. Each of them has specific advantages and disadvantages.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures




References
-
- van Dongen JJ, Seriu T, Panzer-Grümayer ER, et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood. Lancet. 1998;352(9142):1731–1738. - PubMed
-
- Cavé H, van der Werff ten Bosch J, Suciu S, et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer–Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer—Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(9):591–598. - PubMed
-
- Coustan-Smith E, Behm FG, Sanchez J, et al. Immunological detection of minimal residual disease in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 1998;351(9102):550–554. - PubMed
-
- Raff T, Gökbuget N, Lüschen S, et al. GMALL Study Group. Molecular relapse in adult standard-risk ALL patients detected by prospective MRD monitoring during and after maintenance treatment: data from the GMALL 06/99 and 07/03 trials. Blood. 2007;109(3):910–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

