Human β-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling: part 3
- PMID: 25999530
- PMCID: PMC4439562
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-1843
Human β-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling: part 3
Abstract
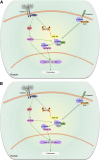
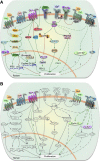
This is the third in a series of Perspectives on intracellular signaling pathways coupled to proliferation in pancreatic β-cells. We contrast the large knowledge base in rodent β-cells with the more limited human database. With the increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes and the recognition that type 2 diabetes is also due in part to a deficiency of functioning β-cells, there is great urgency to identify therapeutic approaches to expand human β-cell numbers. Therapeutic approaches might include stem cell differentiation, transdifferentiation, or expansion of cadaver islets or residual endogenous β-cells. In these Perspectives, we focus on β-cell proliferation. Past Perspectives reviewed fundamental cell cycle regulation and its upstream regulation by insulin/IGF signaling via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling, glucose, glycogen synthase kinase-3 and liver kinase B1, protein kinase Cζ, calcium-calcineurin-nuclear factor of activated T cells, epidermal growth factor/platelet-derived growth factor family members, Wnt/β-catenin, leptin, and estrogen and progesterone. Here, we emphasize Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription, Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-related kinase, cadherins and integrins, G-protein-coupled receptors, and transforming growth factor β signaling. We hope these three Perspectives will serve to introduce these pathways to new researchers and will encourage additional investigators to focus on understanding how to harness key intracellular signaling pathways for therapeutic human β-cell regeneration for diabetes.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK077096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK104211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK55023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK06735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081472/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078060/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080996/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101591/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK67536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

