Therapeutic window of interleukin-2 for autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 25999537
- PMCID: PMC4439560
- DOI: 10.2337/db15-0188
Therapeutic window of interleukin-2 for autoimmune diseases
Figures
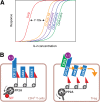
Comment on
-
Selective IL-2 responsiveness of regulatory T cells through multiple intrinsic mechanisms supports the use of low-dose IL-2 therapy in type 1 diabetes.Diabetes. 2015 Jun;64(6):2172-83. doi: 10.2337/db14-1322. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25576057
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008;133:775–787 - PubMed
-
- Gambineri E, Torgerson TR, Ochs HD. Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked inheritance (IPEX), a syndrome of systemic autoimmunity caused by mutations of FOXP3, a critical regulator of T-cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003;15:430–435 - PubMed
-
- Yu A, Snowhite I, Vendrame F, et al. . Selective IL-2 responsiveness of regulatory T cells through multiple intrinsic mechanisms supports the use of low-dose IL-2 therapy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2015;64:2172–2183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

