RNA around the clock - regulation at the RNA level in biological timing
- PMID: 25999975
- PMCID: PMC4419606
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00311
RNA around the clock - regulation at the RNA level in biological timing
Abstract
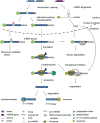
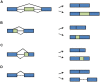
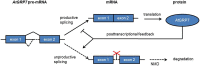
The circadian timing system in plants synchronizes their physiological functions with the environment. This is achieved by a global control of gene expression programs with a considerable part of the transcriptome undergoing 24-h oscillations in steady-state abundance. These circadian oscillations are driven by a set of core clock proteins that generate their own 24-h rhythm through periodic feedback on their own transcription. Additionally, post-transcriptional events are instrumental for oscillations of core clock genes and genes in clock output. Here we provide an update on molecular events at the RNA level that contribute to the 24-h rhythm of the core clock proteins and shape the circadian transcriptome. We focus on the circadian system of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana but also discuss selected regulatory principles in other organisms.
Keywords: RNA-binding protein; circadian oscillation; post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Beyond Transcription: Fine-Tuning of Circadian Timekeeping by Post-Transcriptional Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 10;9(12):616. doi: 10.3390/genes9120616. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-based regulation in the plant circadian clock.Trends Plant Sci. 2011 Oct;16(10):517-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Trends Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 21782493 Review.
-
Circadian clock-regulated expression of an RNA-binding protein in Arabidopsis: characterisation of a minimal promoter element.Mol Gen Genet. 1999 Jun;261(4-5):811-9. doi: 10.1007/s004380050025. Mol Gen Genet. 1999. PMID: 10394919
-
The circadian system of Arabidopsis thaliana: forward and reverse genetic approaches.Chronobiol Int. 1999 Jan;16(1):1-16. doi: 10.3109/07420529908998708. Chronobiol Int. 1999. PMID: 10023572 Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Diurnal Gene Expression in Chinese Cabbage.Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 11;10(2):130. doi: 10.3390/genes10020130. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30754711 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Beyond Transcription: Fine-Tuning of Circadian Timekeeping by Post-Transcriptional Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 10;9(12):616. doi: 10.3390/genes9120616. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide chromatin mapping with size resolution reveals a dynamic sub-nucleosomal landscape in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2017 Sep 13;13(9):e1006988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006988. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28902852 Free PMC article.
-
XAP5 CIRCADIAN TIMEKEEPER regulates RNA splicing and the circadian clock by genetically separable pathways.Plant Physiol. 2023 Jul 3;192(3):2492-2506. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad193. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36974904 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA Methylation in Marine Plants: First Insights and Relevance for Biological Rhythms.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 12;21(20):7508. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207508. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33053767 Free PMC article.
-
Up-Frameshift Protein UPF1 Regulates Neurospora crassa Circadian and Diurnal Growth Rhythms.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1881-1893. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.202788. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28600326 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

