In Vitro Administration of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with MUC-1 Protein Fragment Generates Anticancer Vaccine Response via Macrophage Activation and Polarization Mechanism
- PMID: 26000051
- PMCID: PMC4439945
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.11567
In Vitro Administration of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with MUC-1 Protein Fragment Generates Anticancer Vaccine Response via Macrophage Activation and Polarization Mechanism
Abstract
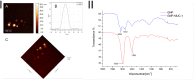
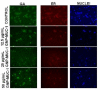
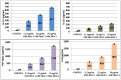
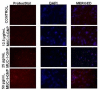
Therapeutic cancer vaccines (or active immunotherapy) aim to guide the patient's personal immune system to eradicate cancer cells. An exciting approach to cancer vaccines has been offered by nanoscale drug delivery systems containing tumor associated antigens (TAAs). Their capacity to stimulate the immune system has been suggested during late years. However, the role of the macrophages as key-elements in antigen-presentation process following TAAs-containing nanosystems is not completely understood. We aimed to evaluate the effect of gold nanoparticles functionalized with mucin-1 peptide (MUC-1) on murine peritoneal macrophages. Gold nanoparticles, obtained using a modified Turkevich method, were functionalized with MUC-1 protein using Clealand's reagent. The obtained GNP-MUC-1 solution was used to treat at various concentrations monolayers of peritoneum-derived macrophages that were further analyzed using confocal and hyperspectral microscopy, ELISA assays and spectroscopic techniques. The GNP-MUC-1 nano-construct had proven to function as a powerful macrophage activator with consequent release of cytokines such as: TNF-ɑ, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12 on peritoneal macrophages we have isolated from mice. Our results demonstrate optimization of antigen-presenting process and predominant M1 polarization following exposure GNP-MUC-1. To our best knowledge this is the first study to evaluate the anticancer effects of a newly designed nano-biocompound on the complex antigen- processing apparatus of peritoneal macrophages.
Keywords: cancer vaccine; macrophages; monoclonal antibodies; peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Mocan L, Ilie I, Tabaran FA. et al. Surface plasmon resonance-induced photoactivation of gold nanoparticles as mitochondria-targeted therapeutic agents for pancreatic cancer. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2013:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Iancu C, Ilie IR, Georgescu CE. et al. Applications of Nanomaterials in Cell Stem Therapies and the Onset of Nanomedicine. Particul Sci Technol. 2009;27(6):562–574.
-
- Nanda R, Chennamaneni P, Gibson J. et al. Abstract P2-16-21: A randomized phase I trial of nanoparticle albumin bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel, Abraxane®) with or without mifepristone for advanced breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(24 Supplement):P2–16. -21-P2-16-21.
-
- Fuller S, Stewart S, Lebowitz M, Malhotra K, Ghanbari H. Inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by a nanoparticle-based therapeutic cancer vaccine targeting HAAH. Journal for immunotherapy of cancer. 2013;1(Suppl 1):P269.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

