Naturally occurring marine brominated indoles are aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands/agonists
- PMID: 26001051
- PMCID: PMC4469569
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00003
Naturally occurring marine brominated indoles are aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands/agonists
Abstract
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that mediates the toxic and biological effects of structurally diverse chemicals, including the environmental contaminant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). As part of a larger effort to identify the full spectrum of chemicals that can bind to and activate the AhR, we have examined the ability of several naturally occurring marine-derived brominated indoles and brominated (methylthio)indoles (collectively referred to as brominated indoles) to bind to the AhR and stimulate AhR-dependent gene expression. Incubation of mouse, rat, and guinea pig recombinant cell lines containing a stably transfected AhR-responsive luciferase reporter gene with eight brominated indoles revealed that all compounds stimulated luciferase reporter gene activity, although some species-specific differences were observed. All compounds induced significantly more luciferase activity when incubated with cells for 4 h as compared to 24 h, demonstrating that these compounds are transient activators of the AhR signaling pathway. Three of the brominated indoles induced CYP1A1 mRNA in human HepG2 cells in vitro and Cyp1a mRNA in zebrafish embryos in vivo. The identification of the brominated indoles as direct ligands and activators/agonists of the AhR was confirmed by their ability to compete with [(3)H]TCDD for binding to the AhR and to stimulate AhR transformation and DNA binding in vitro. Taken together, these results indicate that marine-derived brominated indoles are members of a new class of naturally occurring AhR agonists.
Figures

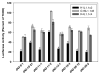

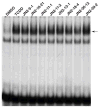
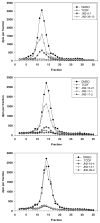
 ) of 0.2 μM TCDF, or 5 μM of each brominated indole for 1 h on ice. Aliquots (300 μl) of each incubation were analyzed for ligand binding by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.
) of 0.2 μM TCDF, or 5 μM of each brominated indole for 1 h on ice. Aliquots (300 μl) of each incubation were analyzed for ligand binding by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.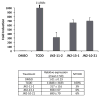
Similar articles
-
Nucleotide specificity of DNA binding of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor:ARNT complex is unaffected by ligand structure.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jan;137(1):102-13. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft234. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24136190 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of diuron and related substituted phenylureas with the Ah receptor pathway.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2006;20(3):103-13. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20126. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16788953 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenosides are novel naturally-occurring aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e66258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066258. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776647 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:309-34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.135828. Epub 2002 Jan 10. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12540743 Review.
-
The Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis.J Cutan Med Surg. 2024 May-Jun;28(3):276-286. doi: 10.1177/12034754241239050. Epub 2024 Mar 18. J Cutan Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38497283 Review.
Cited by
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: a multifunctional chemical sensor for host defense and homeostatic maintenance.Exp Anim. 2017 May 3;66(2):75-89. doi: 10.1538/expanim.16-0092. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Exp Anim. 2017. PMID: 27980293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of marine-derived halogenated indoles as ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Toxicol Rep. 2022 May 25;9:1198-1203. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.05.016. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36518459 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Pharmacology in 2014-2015: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, Antiviral, and Anthelmintic Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action.Mar Drugs. 2019 Dec 19;18(1):5. doi: 10.3390/md18010005. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31861527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbial Catabolites of Tryptophan Are Ligands and Agonists of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: A Detailed Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 9;21(7):2614. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072614. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32283770 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Colonic Mucosal Injury in 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin Poly ADP-Ribose Polymerase (TIPARP/PARP7)-Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 15;23(2):920. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020920. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perdew GH. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:13802–13805. - PubMed
-
- Kazlauskas A, Poellinger L, Pongratz I. Evidence that the co-chaperone p23 regulates ligand responsiveness of the dioxin (aryl hydrocarbon) receptor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13519–13524. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, Fisher JM, Whitlock JP., Jr The DNA recognition site for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:17221–17224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

