Naturally occurring marine brominated indoles are aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands/agonists
- PMID: 26001051
- PMCID: PMC4469569
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00003
Naturally occurring marine brominated indoles are aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands/agonists
Abstract
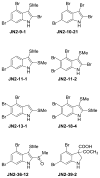
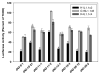
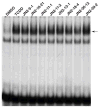
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that mediates the toxic and biological effects of structurally diverse chemicals, including the environmental contaminant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). As part of a larger effort to identify the full spectrum of chemicals that can bind to and activate the AhR, we have examined the ability of several naturally occurring marine-derived brominated indoles and brominated (methylthio)indoles (collectively referred to as brominated indoles) to bind to the AhR and stimulate AhR-dependent gene expression. Incubation of mouse, rat, and guinea pig recombinant cell lines containing a stably transfected AhR-responsive luciferase reporter gene with eight brominated indoles revealed that all compounds stimulated luciferase reporter gene activity, although some species-specific differences were observed. All compounds induced significantly more luciferase activity when incubated with cells for 4 h as compared to 24 h, demonstrating that these compounds are transient activators of the AhR signaling pathway. Three of the brominated indoles induced CYP1A1 mRNA in human HepG2 cells in vitro and Cyp1a mRNA in zebrafish embryos in vivo. The identification of the brominated indoles as direct ligands and activators/agonists of the AhR was confirmed by their ability to compete with [(3)H]TCDD for binding to the AhR and to stimulate AhR transformation and DNA binding in vitro. Taken together, these results indicate that marine-derived brominated indoles are members of a new class of naturally occurring AhR agonists.
Figures


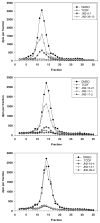
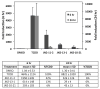
 ) of 0.2 μM TCDF, or 5 μM of each brominated indole for 1 h on ice. Aliquots (300 μl) of each incubation were analyzed for ligand binding by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.
) of 0.2 μM TCDF, or 5 μM of each brominated indole for 1 h on ice. Aliquots (300 μl) of each incubation were analyzed for ligand binding by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.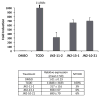
References
-
- Perdew GH. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:13802–13805. - PubMed
-
- Kazlauskas A, Poellinger L, Pongratz I. Evidence that the co-chaperone p23 regulates ligand responsiveness of the dioxin (aryl hydrocarbon) receptor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13519–13524. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, Fisher JM, Whitlock JP., Jr The DNA recognition site for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:17221–17224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

