p63 drives invasion in keratinocytes expressing HPV16 E6/E7 genes through regulation of Src-FAK signalling
- PMID: 26001294
- PMCID: PMC5369957
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3892
p63 drives invasion in keratinocytes expressing HPV16 E6/E7 genes through regulation of Src-FAK signalling
Abstract
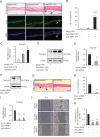
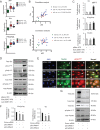
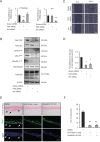
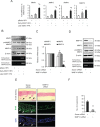
Using microarray information from oro-pharyngeal data sets and results from primary human foreskin keratinocytes (HFK) expressing Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-16 E6/E7 proteins, we show that p63 expression regulates signalling molecules which initiate cell migration such as Src and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and induce invasion in 3D-organotypic rafts; a phenotype that can be reversed by depletion of p63. Knockdown of Src or FAK in the invasive cells restored focal adhesion protein paxillin at cell periphery and impaired the cell migration. In addition, specific inhibition of FAK (PF573228) or Src (dasatinib) activities mitigated invasion and attenuated the expression/activity of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14), a pivotal MMP in the MMP activation cascade. Expression of constitutively active Src in non-invasive HFK expressing E6/E7 proteins upregulated the activity of c-Jun and MMP14, and induced invasion in rafts. Depletion of Src, FAK or AKT in the invasive cells normalised the expression/activity of c-Jun and MMP14, thus implicating the Src-FAK/AKT/AP-1 signalling in MMP14-mediated extra-cellular matrix remodelling. Up-regulation of Src, AP-1, MMP14 and p63 expression was confirmed in oro-pharyngeal cancer. Since p63 transcriptionally regulated expression of many of the genes in this signalling pathway, it suggests that it has a central role in cancer progression.
Keywords: HPV16; MMP14; Src; invasion; p63.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
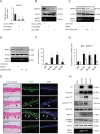
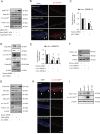
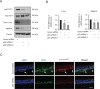
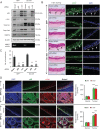
Similar articles
-
Activation of Src, Fyn and Yes non-receptor tyrosine kinases in keratinocytes expressing human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 E7 oncoprotein.Virol J. 2013 Mar 7;10:79. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-79. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23497302 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes HPV 16 E6 oncogene-mediated oropharyngeal cell carcinoma survival and chemoresistance.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:180-200. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30077625
-
Molecular genetic characterization of p53 mutated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells transformed with human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes.Int J Oncol. 2013 Aug;43(2):383-93. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1953. Epub 2013 May 24. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23708675 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein 2 (CRABP2), Up-regulated by HPV E6/E7, Leads to Aberrant Activation of the Integrin β1/FAK/ERK Signaling Pathway and Aggravates the Malignant Phenotypes of Cervical Cancer.Biochem Genet. 2024 Aug;62(4):2686-2701. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10568-6. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38001389
-
Identification of miRNAs dysregulated in human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs) expressing the human papillomavirus (HPV) Type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins.Microrna. 2013;2(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/2211536611302010002. Microrna. 2013. PMID: 25070710
Cited by
-
The Not-So-Good, the Bad and the Ugly: HPV E5, E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in the Orchestration of Carcinogenesis.Viruses. 2021 Sep 22;13(10):1892. doi: 10.3390/v13101892. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPV - A different view on Head and Neck Cancer.Laryngorhinootologie. 2018 Mar;97(S 01):S48-S113. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-121596. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Laryngorhinootologie. 2018. PMID: 29905354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Therapeutic Prospect.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 9;13:10207-10220. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S270342. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of basal cell fate during productive and transforming HPV-16 infection is mediated by progressive E6-driven depletion of Notch.J Pathol. 2017 Aug;242(4):448-462. doi: 10.1002/path.4917. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28497579 Free PMC article.
-
Biological functions and clinical significance of the newly identified long non‑coding RNA RP1‑85F18.6 in colorectal cancer.Oncol Rep. 2018 Nov;40(5):2648-2658. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6694. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30226619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008 GLOBOCAN. Int J Cancer. 2008;2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Gillison ML, Koch WM, Capone RB, Spafford M, Westra WH, Wu L, Zahurak ML, Daniel RW, Viglione M, Symer DE, Shah KV, Sidransky D. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:709–720. - PubMed
-
- Brunner HG, Hamel BCJ, van Bokhoven H. P63 gene mutations and human developmental syndromes. Am J Med Genet. 2002;112:284–290. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

