Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
- PMID: 26001391
- PMCID: PMC4571783
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0465
Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Abstract
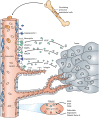
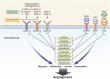
Angiogenesis, or the formation of new capillary blood vessels, occurs primarily during human development and reproduction; however, aberrant regulation of angiogenesis is also a fundamental process found in several pathologic conditions, including cancer. As a process required for invasion and metastasis, tumor angiogenesis constitutes an important point of control of cancer progression. Although not yet completely understood, the complex process of tumor angiogenesis involves highly regulated orchestration of multiple signaling pathways. The proangiogenic signaling molecule vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its cognate receptor (VEGF receptor 2 [VEGFR-2]) play a central role in angiogenesis and often are highly expressed in human cancers, and initial clinical efforts to develop antiangiogenic treatments focused largely on inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR signaling. Such approaches, however, often lead to transient responses and further disease progression because angiogenesis is regulated by multiple pathways that are able to compensate for each other when single pathways are inhibited. The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor (PDGFR) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and FGF receptor (FGFR) pathways, for example, provide potential escape mechanisms from anti-VEGF/VEGFR therapy that could facilitate resumption of tumor growth. Accordingly, more recent treatments have focused on inhibiting multiple signaling pathways simultaneously. This comprehensive review discusses the limitations of inhibiting VEGF signaling alone as an antiangiogenic strategy, the importance of other angiogenic pathways including PDGF/PDGFR and FGF/FGFR, and the novel current and emerging agents that target multiple angiogenic pathways for the treatment of advanced solid tumors.
Implications for practice: Significant advances in cancer treatment have been achieved with the development of antiangiogenic agents, the majority of which have focused on inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway. VEGF targeting alone, however, has not proven to be as efficacious as originally hoped, and it is increasingly clear that there are many interconnected and compensatory pathways that can overcome VEGF-targeted inhibition of angiogenesis. Maximizing the potential of antiangiogenic therapy is likely to require a broader therapeutic approach using a new generation of multitargeted antiangiogenic agents.
Keywords: Angiogenesis inhibitors; Antibodies, monoclonal, humanized; Fibroblast growth factor; Molecular targeted therapy; Platelet-derived growth factor; Receptors; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
©AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):333-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24139944 Review.
-
Anti-FGF2 approaches as a strategy to compensate resistance to anti-VEGF therapy: long-pentraxin 3 as a novel antiangiogenic FGF2-antagonist.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009 Dec;20(4):225-34. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2009.0175. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009. PMID: 20167562 Review.
-
The potential of fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling as a therapeutic target in tumor angiogenesis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(10):1361-77. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1062475. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 26125971 Review.
-
Antiangiogenic therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncologist. 2013;18(4):430-8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0388. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23576483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways governing tumor angiogenesis.Oncology. 2011;81 Suppl 1:24-9. doi: 10.1159/000333256. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Oncology. 2011. PMID: 22212932 Review.
Cited by
-
Charge-Transfer Complex of Linifanib with 2,3-dichloro-3,5-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone: Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, Computational Molecular Modelling and Application in the Development of Novel 96-microwell Spectrophotometric Assay.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Mar 12;15:1167-1180. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S296502. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33737805 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted anti-angiogenesis therapy for advanced osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 26;14:1413213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1413213. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39252946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Both p53 codon 72 Arg/Arg and pro/Arg genotypes in glioblastoma multiforme are associated with a better prognosis in bevacizumab treatment.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 29;20(1):709. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07210-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32727419 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Mathematical Modelling for Glioblastoma: A Critical Review and a Patient-Specific Case.J Clin Med. 2021 May 17;10(10):2169. doi: 10.3390/jcm10102169. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34067871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering vascularised organoid-on-a-chip: strategies, advances and future perspectives.Biomater Transl. 2024 Mar 28;5(1):21-32. doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2024.01.003. eCollection 2024. Biomater Transl. 2024. PMID: 39220668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis: An organizing principle for drug discovery? Nature Rev Drug Discov . 2007;6:273–286. - PubMed
-
- Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1011–1027. - PubMed
-
- Avastin [prescribing information]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

