Antibacterial activity of native California medicinal plant extracts isolated from Rhamnus californica and Umbellularia californica
- PMID: 26001558
- PMCID: PMC4443625
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-015-0086-0
Antibacterial activity of native California medicinal plant extracts isolated from Rhamnus californica and Umbellularia californica
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major threat to global public health. Medicinal plants have long been used as remedies for infectious diseases by native cultures around the world and have the potential for providing effective treatments for antibiotic-resistant infections. Rhamnus californica (Rhamnaceae) and Umbellularia californica (Lauraceae) are two indigenous California plant species historically used by Native Americans to treat skin, respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. This study aimed to assess the in vitro antimicrobial activity of methanolic extracts of leaves and bark of R. and U. californica against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Methods: Methanolic extracts of leaves and bark of R. and U. californica were prepared by soxhlet extraction and evaluated for their antimicrobial activity against Bacillus cereus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Mycobacterium smegmatis, Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa using disc diffusion and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays. Chemical profiling of the extracts was performed using standard methods.
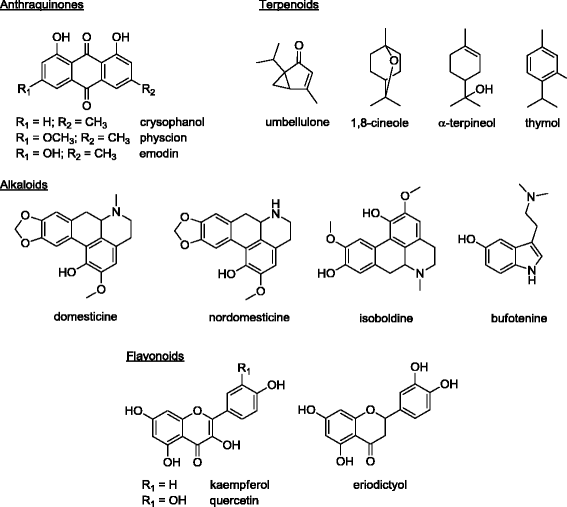
Results: All extracts inhibited the growth of MRSA and other Gram-positive bacteria with MICs of 3.3-6.0 mg/ml. Gram-negative organisms were unaffected by these extracts. U. californica extracts (leaves and bark) had the lowest MIC values. Chemical profiling detected the presence of quinones, alkaloids, flavonoids, cardenolides, tannins and saponins in these extracts. Our study is the first to report the antimicrobial properties of R. and U. californica and illustrates their promising anti-MRSA potential.
Conclusions: Our results give scientific credence to the traditional medicinal uses of these plants by the indigenous peoples of California. Further investigation of the secondary metabolites responsible for the antimicrobial activity of these extracts against MRSA is warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological properties and protein binding capacity of phenolic extracts of some Venda medicinal plants used against cough and fever.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Aug 30;143(1):185-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.022. Epub 2012 Jun 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22732728
-
In vitro screening of five local medicinal plants for antibacterial activity using disc diffusion method.Trop Biomed. 2005 Dec;22(2):165-70. Trop Biomed. 2005. PMID: 16883283
-
Investigations of antimicrobial activity of some Cameroonian medicinal plant extracts against bacteria and yeast with gastrointestinal relevance.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jun 26;142(1):265-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.05.005. Epub 2012 May 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22583961
-
Novel antibacterial modalities against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus derived from plants.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S153-S161. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1541865. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30501508 Review.
-
Phytoextracts as Antibacterials: A Review.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020;17(4):523-533. doi: 10.2174/1570163816666191106103730. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020. PMID: 31702527 Review.
Cited by
-
Latin American Plants against Microorganisms.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;12(23):3997. doi: 10.3390/plants12233997. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ARF1-binding factor triggering programmed cell death and periderm development in pear russet fruit skin.Hortic Res. 2022 Jan 19;9:uhab061. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhab061. Online ahead of print. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 35043172 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Screening of 239 Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plant Extracts for Their Antibacterial Activities against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cytotoxic Activities.Pathogens. 2020 Mar 4;9(3):185. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9030185. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32143422 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity study of Musizin isolated from Rhamnus wightii Wight and Arn.Bioinformation. 2018 Dec 21;14(9):511-520. doi: 10.6026/97320630014511. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 31223211 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antibacterial Potentials and Chemical Composition of Salvia officinalis and Mentha suaveolens Grown Wild in Morocco.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022 Jun 15;2022:2844880. doi: 10.1155/2022/2844880. eCollection 2022. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. In: Fact Sheet No 194. 2014. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs194/en/. Accessed 07 Aug 2014.
-
- Moerman DE. Native American medicinal plant : an ethnobotanical dictionary. Portland, Or: Timber Press; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical