Clinical efficacy and safety of monthly oral ibandronate 100 mg versus monthly intravenous ibandronate 1 mg in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis
- PMID: 26001561
- PMCID: PMC4605968
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-015-3175-1
Clinical efficacy and safety of monthly oral ibandronate 100 mg versus monthly intravenous ibandronate 1 mg in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis
Abstract
The MOVEST study evaluated the efficacy and safety of monthly oral ibandronate versus licensed monthly IV ibandronate in Japanese osteoporotic patients. Relative BMD gains after 12 months were 5.22 % oral and 5.34 % IV, showing non-inferiority of oral to IV ibandronate (primary endpoint). No new safety concerns were identified.
Introduction: The randomized, phase 3, double-blind MOVEST (Monthly Oral VErsus intravenouS ibandronaTe) study evaluated the efficacy and safety of monthly oral ibandronate versus the licensed monthly intravenous (IV) ibandronate regimen in Japanese patients with osteoporosis.
Methods: Ambulatory patients aged ≥ 55 years with primary osteoporosis were randomized to receive oral ibandronate 100 mg/month plus monthly IV placebo, or IV ibandronate 1 mg/month plus monthly oral placebo. The primary endpoint was non-inferiority of oral versus IV ibandronate with respect to bone mineral density (BMD) gains at the lumbar spine after 12 months of treatment.
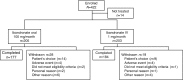
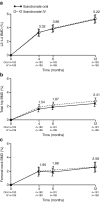
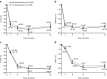
Results: Four hundred twenty-two patients were enrolled with 372 patients in the per-protocol set (183 and 189 in the oral and IV ibandronate groups, respectively). The relative change from baseline in lumbar spine BMD values for the oral and IV ibandronate groups, respectively, was 5.22 % (95 % confidence interval [CI] 4.65, 5.80) and 5.34 % (95 % CI 4.78, 5.90). The least squares mean difference between the two groups was -0.23 % (95 % CI -0.97, 0.51), showing non-inferiority of oral ibandronate to IV ibandronate (non-inferiority limit = -1.60). Changes in BMD values at other sites, and bone turnover marker levels in the oral ibandronate group, were comparable with those of the IV group. The safety profile was similar to that previously demonstrated; no new safety concerns were identified.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the non-inferiority of oral ibandronate 100 mg/month to IV ibandronate 1 mg/month (licensed dose in Japan) in increasing lumbar spine BMD in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis.
Keywords: Ibandronate; MOVEST study; Oral dosing; Osteoporosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and tolerability of once-monthly oral ibandronate (150 mg) and once-weekly oral alendronate (70 mg): additional results from the Monthly Oral Therapy With Ibandronate For Osteoporosis Intervention (MOTION) study.Clin Ther. 2009 Apr;31(4):751-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.04.018. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19446148 Clinical Trial.
-
Monthly oral ibandronate 100 mg is as effective as monthly intravenous ibandronate 1 mg in patients with various pathologies in the MOVEST study.J Bone Miner Metab. 2018 May;36(3):336-343. doi: 10.1007/s00774-017-0839-2. Epub 2017 Apr 7. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018. PMID: 28389932 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of intravenous ibandronate injections in postmenopausal osteoporosis: 2-year results from the DIVA study.J Rheumatol. 2008 Mar;35(3):488-97. Epub 2008 Feb 1. J Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18260172 Clinical Trial.
-
Ibandronate: A Review in Japanese Patients with Osteoporosis.Drugs Aging. 2016 Apr;33(4):295-303. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0360-7. Drugs Aging. 2016. PMID: 26915075 Review.
-
Update on monthly oral bisphosphonate therapy for the treatment of osteoporosis: focus on ibandronate 150 mg and risedronate 150 mg.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Dec;25(12):2951-60. doi: 10.1185/03007990903361307. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19835464 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of monthly intravenous ibandronate injections in a real-world setting: Subgroup analysis of a postmarketing observational study.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2019 Mar;5(1):11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2019. PMID: 31008373 Free PMC article.
-
Ibandronate Suppresses Changes in Apatite Orientation and Young's Modulus Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Rat Vertebrae.Calcif Tissue Int. 2022 Jun;110(6):736-745. doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00940-2. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022. PMID: 34989822 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of effectiveness and safety of ibandronate and minodronate combined with eldecalcitol in primary osteoporosis of women: A 1-year follow-up study.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2017 Mar;3(1):37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2016.12.002. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2017. PMID: 30775501 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with inadequate responses to risedronate in Japanese patients with osteoporosis.J Bone Miner Metab. 2019 Jan;37(1):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s00774-018-0931-2. Epub 2018 May 8. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019. PMID: 29737412
-
Safety and effectiveness of monthly intravenous ibandronate injections in a prospective, postmarketing, and observational study in Japanese patients with osteoporosis.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2018 Mar;4(1):22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2018. PMID: 30775537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chesnut CH, III, Skag A, Christiansen C, Recker R, Stakkestad JA, Hoiseth A, Felsenberg D, Huss H, Gilbride J, Schimmer RC, Delmas PD, Oral Ibandronate Osteoporosis Vertebral Fracture Trial in North America and Europe (BONE) Effects of oral ibandronate administered daily or intermittently on fracture risk in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19:1241–1249. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040325. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reginster JY, Adami S, Lakatos P, Greenwald M, Stepan JJ, Silverman SL, Christiansen C, Rowell L, Mairon N, Bonvoisin B, Drezner MK, Emkey R, Felsenberg D, Cooper C, Delmas PD, Miller PD. Efficacy and tolerability of once-monthly oral ibandronate in postmenopausal osteoporosis: 2 year results from the MOBILE study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:654–661. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.044958. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eisman JA, Civitelli R, Adami S, Czerwinski E, Recknor C, Prince R, Reginster JY, Zaidi M, Felsenberg D, Hughes C, Mairon N, Masanauskaite D, Reid DM, Delmas PD, Recker RR. Efficacy and tolerability of intravenous ibandronate injections in postmenopausal osteoporosis: 2-year results from the DIVA study. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:488–497. - PubMed
-
- Delmas PD, Adami S, Strugala C, Stakkestad JA, Reginster JY, Felsenberg D, Christiansen C, Civitelli R, Drezner MK, Recker RR, Bolognese M, Hughes C, Masanauskaite D, Ward P, Sambrook P, Reid DM. Intravenous ibandronate injections in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: one-year results from the dosing intravenous administration study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1838–1846. doi: 10.1002/art.21918. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

