A case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and bile duct carcinoma treated with a combination of sunitinib and gemcitabine
- PMID: 26001650
- PMCID: PMC4491890
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1443-2
A case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and bile duct carcinoma treated with a combination of sunitinib and gemcitabine
Abstract
Background: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) had been a chemo-refractory disease, but recent advances in multiple kinase inhibitors such as sunitinib have dramatically changed the clinical course of mRCC. Sunitinib is used for mRCC chemotherapy based on the favorable results of a recent clinical trial, but specific biomarkers predicting efficacy and safety are not yet available. Locally advanced bile duct carcinoma (BDC) has generally been treated with single agent gemcitabine or as doublet therapy with cisplatin. Concomitant occurrence of mRCC and BDC is extremely rare, and a standard therapeutic strategy has not been established.
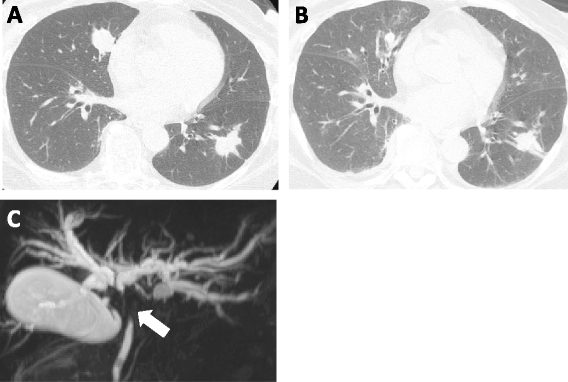
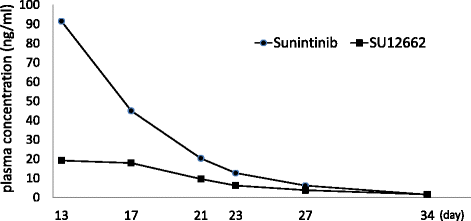
Case presentation: A 65-year-old woman was diagnosed as having multiple mRCC and intercurrent, locally advanced BDC. A single course of combination therapy with sunitinib (25 mg/day, day2-15) and gemcitabine (750 mg/m(2), days 1, 8) was administered, and this showed obvious effects, with partial response for mRCC and stable disease for BDC. However, the patient also experienced severe adverse events, including hematological and various non-hematological toxicities; the combination therapy was then terminated on day 13 after its initiation. She recovered on day 28 and is alive 3.5 years after the diagnosis. The plasma trough levels of sunitinib and its active metabolite SU12662 on day 13 were 91.5 ng/mL and 19.2 ng/mL, respectively, which were relatively higher than in previous reports. Analysis of her single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detected TC in ABCB1 3435C/T, TC in 1236C/T and TT in 2677G/T, suggesting a possible TTT haplotype.
Conclusion: A rare case of double cancer of mRCC and BDC was treated by combination chemotherapy. Although unknown synergistic mechanisms of these agents may be involved, severe toxicities might be possibly associated with high sunitinib exposure. Further exploration of combination therapy with sunitinib and gemcitabine is required.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

