Impact of gestational age, sex, and postnatal age on urine biomarkers in premature neonates
- PMID: 26001700
- PMCID: PMC4581905
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-015-3129-z
Impact of gestational age, sex, and postnatal age on urine biomarkers in premature neonates
Abstract
Background: Urine proteins may help in understanding physiology and diagnosing disease in premature infants. Determining how urine proteins vary by degree of prematurity, sex, and postnatal day is warranted.
Methods: We performed a prospective cohort study to assess the independent correlation of 14 urine biomarkers (measured on postnatal days 1-4) with gestational age (GA), sex, and postnatal age in 81 premature infants (mean, 1017 g) without acute kidney injury using a random-effects mixed model.
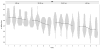
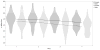
Results: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) showed significant associations for sex, GA, and postnatal age. Cystatin C, osteopontin (OPN), and trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) were associated with postnatal age and GA, but not sex. Epithelial growth factor (EGF) and uromodulin were associated with GA only. Clusterin was associated with postnatal age and sex. Albumin was associated with sex only. Beta-2-microglbulin (B2M), osteoactivin, kidney injury molecule -1 (KIM-1), and alpha glutathione S-transferase (αGST) were associated with postnatal age only.
Conclusions: Postnatal age affects B2M, cystatin C, NGAL, OPN, clusterin, Kim-1, osteoactivin, TFF3, VEGF, αGST. GA affects cystatin C, EGF, NGAL, OPN, UMOD, TFF3, and VEGF. Sex affects albumin, NGAL, and clusterin. Interpretation of urine biomarkers will need to account for these associations.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Acute renal failure; Baseline; Cystatin C; Infant; KIM-1; NGAL; Reference.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Shemin D, Dworkin LDZ. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for early acute kidney injury. Crit Care Clin. 2011;27:379–389. - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Garg AX. Testing new biomarkers for acute kidney injury: association, prediction, and intervention. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:987–989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1TR00165/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000165/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD066982/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD067126/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE013608/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK13608-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079337/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001417/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK079337/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

