Vision-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Ocular Graft-versus-Host Disease
- PMID: 26001816
- PMCID: PMC4516685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.04.011
Vision-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Ocular Graft-versus-Host Disease
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the vision-related quality of life (QOL) in a cohort of patients with ocular graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Design: Prospective study.
Participants: Eighty-four patients diagnosed with chronic ocular GVHD.
Methods: We assessed the vision-related QOL with the 25-item National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI-VFQ-25). The symptoms of ocular GVHD were assessed using the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) and Symptom Assessment in Dry Eye (SANDE) questionnaires.
Main outcome measures: We assessed vision-related QOL with the NEI-VFQ-25 and compared the scores obtained from patients with ocular GVHD with those from a healthy population. In the ocular GVHD population, we also evaluated the associations between the NEI-VFQ-25 and the dry eye symptoms measured by the OSDI and SANDE questionnaires, age, duration of disease, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), corneal fluorescein staining (CFS), tear break-up time, and Schirmer test.
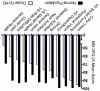
Results: The mean composite NEI-VFQ-25 score in patients with ocular GVHD was 76.5±17. Compared with healthy subjects, patients with ocular GVHD reported reduced scores on all NEI-VFQ-25 subscales (each P < 0.001) with the exception of color vision (P = 0.11). The NEI-VFQ-25 composite scores significantly correlated with OSDI (R = -0.81, P < 0.001), SANDE (R = -0.56, P < 0.001), CFS (R = -0.36, P = 0.001), and BCVA (R = -0.30, P = 0.004).
Conclusions: Patients with ocular GVHD experience measurable impairment of vision-related QOL. This study highlights the impact of ocular GVHD on the vision-related QOL, and thus the importance of comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Copyright © 2015 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Appelbaum FR. Hematopoietic-cell transplantation at 50. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1472–5. - PubMed
-
- Kansu E. The pathophysiology of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Int J Hematol. 2004;79:209–15. - PubMed
-
- Pallua S, Giesinger J, Oberguggenberger A, et al. Impact of GvHD on quality of life in long-term survivors of haematopoietic transplantation. Bone marrow transplantation. 2010;45:1534–9. - PubMed
-
- Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation. 2005;11:945–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

