Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice
- PMID: 26001832
- PMCID: PMC4465309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-015-0324-6
Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice
Abstract
Background: Heat stress induces many pathophysiological responses and has a profound impact on brain structure. It has been demonstrated that exposure to high temperature induces cognitive impairment in experimental animals and humans. Although the effects of heat stress have long been studied, the mechanisms by which heat stress affects brain structure and cognition not well understood.
Methods: In our longitudinal study of mice exposed to heat over 7, 14, or 42 days, we found that heat stress time dependently impaired cognitive function as determined by Y-maze, passive avoidance, and novel object recognition tests. To elucidate the histological mechanism by which thermal stress inhibited cognitive abilities, we examined heat stress-induced inflammation in the hippocampus.
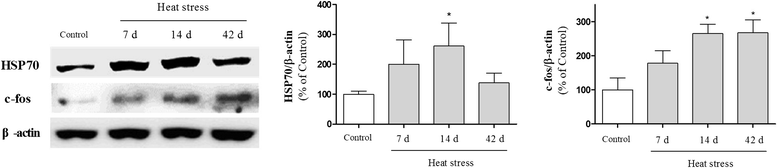
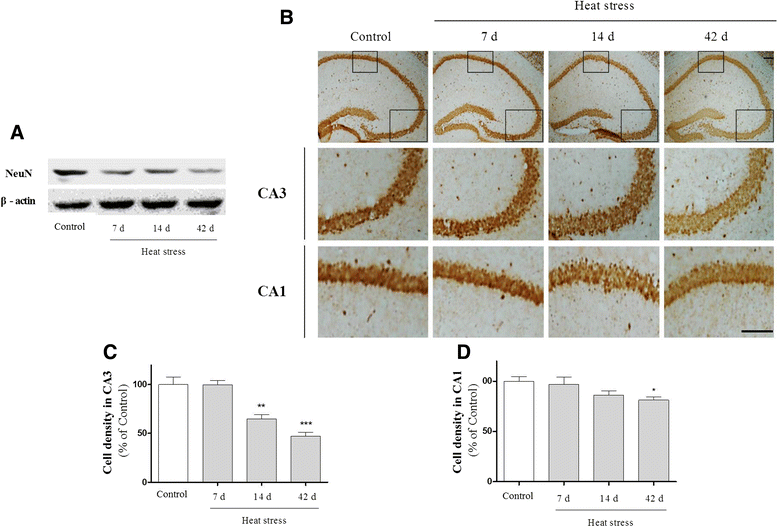
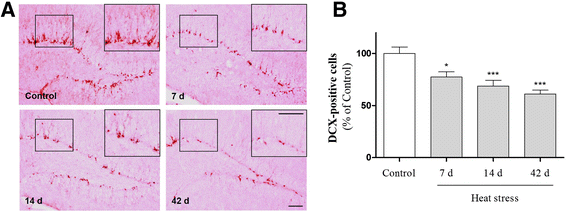
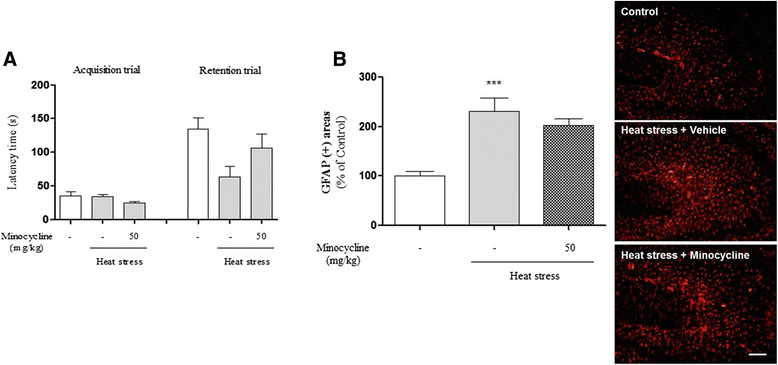
Results: In mice subjected to heat exposure, we found: 1) an increased number of glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP)- and macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1)-positive cells, 2) up-regulated nuclear factor (NF)-κB, a master regulator of inflammation, and 3) marked increases in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the mouse hippocampus. We also observed that neuronal and synaptic densities were degenerated significantly in hippocampal regions after heat exposure, as determined by histological analysis of neuronal nuclei (NeuN), postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95), and synaptophysin expression. Moreover, in heat-exposed mice, we found that the number of cells positive for doublecortin (DCX), a marker of neurogenesis, was significantly decreased compared with control mice. Finally, anti-inflammatory agent minocycline inhibited the heat stress-induced cognitive deficits and astogliosis in mice.
Conclusions: Together, these findings suggest that heat stress can lead to activation of glial cells and induction of inflammatory molecules in the hippocampus, which may act as causative factors for memory loss, neuronal death, and impaired adult neurogenesis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
IL-17A is implicated in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in aged rats via microglial activation.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Sep 15;12:165. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0394-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26373740 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of sinapic acid through the suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygase-2, and proinflammatory cytokines expressions via nuclear factor-kappaB inactivation.J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Nov 12;56(21):10265-72. doi: 10.1021/jf802095g. Epub 2008 Oct 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. PMID: 18841975
-
Evidence for the contribution of adult neurogenesis and hippocampal cell death in experimental cerebral malaria cognitive outcome.Neuroscience. 2015 Jan 22;284:920-933. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.10.062. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25451296
-
Neuroinflammation negatively affects adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition: can exercise compensate?Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Feb;61:121-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 26695382 Review.
-
Effect of Heat Stress on Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Insights into the Cellular and Molecular Basis of Neuroinflammation-Induced Deficits.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01165-5. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 34767143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heat-Stress Preconditioning Attenuates Behavioral Responses to Psychological Stress: The Role of HSP-70 in Modulating Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4129. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084129. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456946 Free PMC article.
-
Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Dec 30;12(1):16. doi: 10.3390/toxins12010016. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31905825 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplements formulated to prevent cognitive impairment in animals.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Nov 18;5:2294-2308. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.11.004. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36439642 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term exposure to heatwave-like temperatures affects learning and memory in bumblebees.Glob Chang Biol. 2022 Jul;28(14):4251-4259. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16196. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Glob Chang Biol. 2022. PMID: 35429217 Free PMC article.
-
β-Hydroxybutyric acid improves cognitive function in a model of heat stress by promoting adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Stress Biol. 2022 Dec 29;2(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s44154-022-00079-6. Stress Biol. 2022. PMID: 37676574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kregel KC, Tipton CM, Seals DR. Thermal adjustments to nonexertional heat stress in mature and senescent Fischer 344 rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990;68:1337–42. - PubMed
-
- Moran DS, Horowitz M, Meiri U, Laor A, Pandolf KB. The physiological strain index applied to heat-stressed rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1999;86:895–901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

