The validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire for screening depression in chronic care patients in primary health care in South Africa
- PMID: 26001915
- PMCID: PMC4446842
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-015-0503-0
The validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire for screening depression in chronic care patients in primary health care in South Africa
Abstract
Background: People with chronic health conditions are known to have a higher prevalence of depressive disorder. The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) is a widely-used screening tool for depression which has not yet been validated for use on chronic care patients in South Africa.
Methods: A sample of 676 chronic care patients attending two primary health facilities in North West Province, South Africa were administered the PHQ-9 by field workers and a diagnostic interview (the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV) (SCID) by clinical psychologists. The PHQ-9 and the PHQ-2 were evaluated against the SCID, as well as for sub-samples of patients who were being treated for HIV infection and for hypertension.
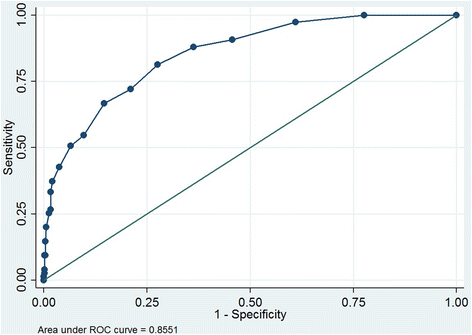
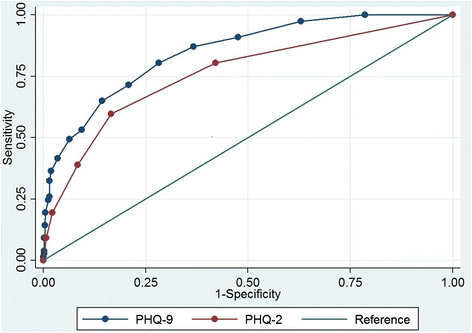
Results: Using the SCID, 11.4 % of patients had major depressive disorder. The internal consistency estimate for the PHQ-9 was 0.76, with an area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC) of 0.85 (95 % CI 0.82-0.88), which was higher than the AURUC for the PHQ-2 (0.76, 95 % CI 0.73-0.79). Using a cut-point of 9, the PHQ-9 has sensitivity of 51 % and specificity of 94 %. The PHQ-9 AUROC for the sub-samples of patients with HIV and with hypertension were comparable (0.85 and 0.86, respectively).
Conclusions: The PHQ-9 is useful as a screening tool for depression among patients receiving treatment for chronic care in a public health facility.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the 10-item Centre for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D-10) in Zulu, Xhosa and Afrikaans populations in South Africa.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 9;17(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1178-x. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28068955 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 to screen for depression in a high-HIV burden primary healthcare clinic in Johannesburg, South Africa.J Affect Disord. 2014;167:160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 12. J Affect Disord. 2014. PMID: 24972364 Free PMC article.
-
Validating screening tools for depression in stroke and transient ischemic attack patients.Int J Psychiatry Med. 2016 Apr;51(3):262-77. doi: 10.1177/0091217416652616. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2016. PMID: 27284119
-
Screening and case finding for major depressive disorder using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): a meta-analysis.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2015 Nov-Dec;37(6):567-76. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26195347 Review.
-
Screening for depression in primary care with Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9): A systematic review.J Affect Disord. 2021 Jan 15;279:473-483. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.09.131. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 33126078
Cited by
-
Diagnostic validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2) among Ethiopian adults.Compr Psychiatry. 2016 Oct;70:216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2016.07.011. Epub 2016 Jul 30. Compr Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27567282 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative care for the detection and management of depression among adults with hypertension in South Africa: study protocol for the PRIME-SA randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Mar 22;19(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2518-6. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29566730 Free PMC article.
-
Investing for population mental health in low and middle income countries-where and why?Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022 Aug 11;16(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13033-022-00547-6. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022. PMID: 35953845 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of the Patient Health Questionnaire scale (PHQ-9) among university students of Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 8;17(6):e0269634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269634. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35675375 Free PMC article.
-
Validating mental health assessment in Kenya using an innovative gold standard.Int J Psychol. 2020 Jun;55(3):425-434. doi: 10.1002/ijop.12604. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Int J Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31209898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ziegelstein RC, Fauerbach JA, Stevens SS, Romanelli J, Richter DP, Bush DE. Patients with depression are less likely to follow recommendations to reduce cardiac risk during recovery from a myocardial infarction. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(12):1818–23. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.12.1818. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources