Structure-guided sequence specificity engineering of the modification-dependent restriction endonuclease LpnPI
- PMID: 26001968
- PMCID: PMC4499157
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv548
Structure-guided sequence specificity engineering of the modification-dependent restriction endonuclease LpnPI
Abstract
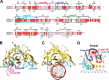
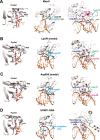
The eukaryotic Set and Ring Associated (SRA) domains and structurally similar DNA recognition domains of prokaryotic cytosine modification-dependent restriction endonucleases recognize methylated, hydroxymethylated or glucosylated cytosine in various sequence contexts. Here, we report the apo-structure of the N-terminal SRA-like domain of the cytosine modification-dependent restriction enzyme LpnPI that recognizes modified cytosine in the 5'-C(mC)DG-3' target sequence (where mC is 5-methylcytosine or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and D = A/T/G). Structure-guided mutational analysis revealed LpnPI residues involved in base-specific interactions and demonstrated binding site plasticity that allowed limited target sequence degeneracy. Furthermore, modular exchange of the LpnPI specificity loops by structural equivalents of related enzymes AspBHI and SgrTI altered sequence specificity of LpnPI. Taken together, our results pave the way for specificity engineering of the cytosine modification-dependent restriction enzymes.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Ohki I., Shimotake N., Fujita N., Jee J., Ikegami T., Nakao M., Shirakawa M. Solution structure of the methyl-CpG binding domain of human MBD1 in complex with methylated DNA. Cell. 2001;105:487–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

