Free and cued memory in relation to biomarker-defined abnormalities in clinically normal older adults and those at risk for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 26002757
- PMCID: PMC4479270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.04.034
Free and cued memory in relation to biomarker-defined abnormalities in clinically normal older adults and those at risk for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objectives: Furthering our understanding of the relationship between amyloidosis (Aβ), neurodegeneration (ND), and cognition is imperative for early identification and early intervention of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the subtle cognitive decline differentially associated with each biomarker-defined stage of preclinical AD has yet to be fully characterized. Recent work indicates that different components of memory performance (free and cued recall) may be differentially specific to memory decline in prodromal AD. We sought to examine the relationship between free and cued recall paradigms, in addition to global composites of memory, executive functioning, and processing speed in relation to stages of preclinical AD.
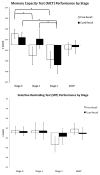
Methods: A total of 260 clinically normal (CN) older adults (CDR=0) from the Harvard Aging Brain study were grouped according to preclinical AD stages including Stage 0 (Aβ-/ND-), Stage 1 (Aβ+/ND-), Stage 2 (Aβ+/ND+), and suspected non-Alzheimer's associated pathology (SNAP; Aβ-/ND+). General linear models controlling for age, sex, and education were used to assess for stage-based performance differences on cognitive composites of executive functioning, processing speed, and memory in addition to free and cued delayed recall on the Selective Reminding Test (SRT) and Memory Capacity Test (MCT).
Results: Global memory performance differed between preclinical stages with Stage 2 performing worse compared with Stage 0. When examining free and cued paradigms by memory test, only the MCT (and not the SRT) revealed group differences. More specifically, Stage 1 was associated with decrements in free recall compared with Stage 0 while Stage 2 was associated with decrements in both free and cued recall. There was a trend for the SNAP group to perform worse on free recall compared with Stage 0. Finally, there was no association between preclinical stage and global composites of executive functioning or processing speed.
Conclusions: Clinically normal older adults with underlying evidence of amyloidosis and neurodegeneration exhibit subtle, yet measurable differences in memory performance, but only on a challenging associative test. The sensitivity of free vs. cued memory paradigms may be dependent on preclinical stage such that reduced free recall is associated with amyloidosis alone (Stage 1) while a decline in cued recall may represent progression to amyloidosis and neurodegeneration (Stage 2). These findings may have practical applications for clinical assessment and clinical trial design.
Keywords: Biomarker stages; Free and cued memory; Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Algarabel S, Fuentes M, Escudero J, Pitarque A, Peset V, Mazón JF, Meléndez JC. Recognition memory deficits in mild cognitive impairment. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition. 2012;19(5):608–619. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS. Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology. 2006;66(12):1837–1844. - PubMed
-
- Benton AL, editor. Contributions to neuropsychological assessment: A clinical manual. Oxford University Press; 1994.
-
- Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, Folstein MF. Population-based norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by age and educational level. Jama. 1993;269(18):2386–2391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50AG0051341/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32AG044054/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG027435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG036694/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034556/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23AG044431/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG037497/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24AG035007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01AG040197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG044431/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG035007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32AG023480-08/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037497/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG036694/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG034556/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AG044054/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG023480/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG040197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

