Changes in Sodium, Calcium, and Magnesium Ion Concentrations That Inhibit Geobacillus Biofilms Have No Effect on Anoxybacillus flavithermus Biofilms
- PMID: 26002898
- PMCID: PMC4495209
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01037-15
Changes in Sodium, Calcium, and Magnesium Ion Concentrations That Inhibit Geobacillus Biofilms Have No Effect on Anoxybacillus flavithermus Biofilms
Abstract
This study investigated the effects of varied sodium, calcium, and magnesium concentrations in specialty milk formulations on biofilm formation by Geobacillus spp. and Anoxybacillus flavithermus. The numbers of attached viable cells (log CFU per square centimeter) after 6 to 18 h of biofilm formation by three dairy-derived strains of Geobacillus and three dairy-derived strains of A. flavithermus were compared in two commercial milk formulations. Milk formulation B had relatively high sodium and low calcium and magnesium concentrations compared with those of milk formulation A, but the two formulations had comparable fat, protein, and lactose concentrations. Biofilm formation by the three Geobacillus isolates was up to 4 log CFU cm(-2) lower in milk formulation B than in milk formulation A after 6 to 18 h, and the difference was often significant (P ≤ 0.05). However, no significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) were found when biofilm formations by the three A. flavithermus isolates were compared in milk formulations A and B. Supplementation of milk formulation A with 100 mM NaCl significantly decreased (P ≤ 0.05) Geobacillus biofilm formation after 6 to 10 h. Furthermore, supplementation of milk formulation B with 2 mM CaCl2 or 2 mM MgCl2 significantly increased (P ≤ 0.05) Geobacillus biofilm formation after 10 to 18 h. It was concluded that relatively high free Na(+) and low free Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) concentrations in milk formulations are collectively required to inhibit biofilm formation by Geobacillus spp., whereas biofilm formation by A. flavithermus is not impacted by typical cation concentration differences of milk formulations.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
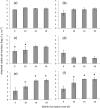
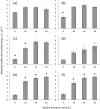
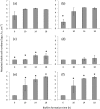

Similar articles
-
Preconditioning with cations increases the attachment of Anoxybacillus flavithermus and Geobacillus species to stainless steel.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jul;79(13):4186-90. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00462-13. Epub 2013 May 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23645192 Free PMC article.
-
Anoxybacillus and Geobacillus biofilms in the dairy industry: effects of surface material, incubation temperature and milk type.Biofouling. 2019 May;35(5):551-560. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2019.1628221. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Biofouling. 2019. PMID: 31273998
-
Influence of cations on growth of thermophilic Geobacillus spp. and Anoxybacillus flavithermus in planktonic culture.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Apr;78(7):2477-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06951-11. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22287005 Free PMC article.
-
Thermophilic bacilli and their importance in dairy processing.Int J Food Microbiol. 2010 Dec 15;144(2):215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.027. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21047695 Review.
-
Magnesium and calcium ions: roles in bacterial cell attachment and biofilm structure maturation.Biofouling. 2019 Oct;35(9):959-974. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2019.1674811. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Biofouling. 2019. PMID: 31687841 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Biofilms in the Food Industry-A Comprehensive Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 19;18(4):2014. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18042014. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33669645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Models for the Biofilm Formation of Geobacillus and Anoxybacillus on Stainless Steel Surface in Whole Milk.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2021 Mar;41(2):288-299. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e100. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2021. PMID: 33987549 Free PMC article.
-
Parageobacillus and Geobacillus spp.: From Food Spoilage to Beneficial Food Applications.Foods. 2025 Aug 9;14(16):2775. doi: 10.3390/foods14162775. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40870688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the Morphological Architecture of Mn2O3 Nanoparticles to MnCoO Nanoflakes by Loading Co3+ Via a Co-Precipitation Approach for Mosquitocidal Development.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;14(3):567. doi: 10.3390/mi14030567. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill BM, Smythe BW. 2012. Endospores of thermophilic bacteria in ingredient milk powders and their significance to the manufacture of sterilized milk products: an industrial perspective. Food Rev Int 28:299–312. doi:10.1080/87559129.2011.635487. - DOI
-
- Hermansson M. 1999. The DLVO theory in microbial adhesion. Colloids Surf B 14:105–119. doi:10.1016/S0927-7765(99)00029-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

