Second generation physical and linkage maps of yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) and comparison of synteny with four model fish
- PMID: 26003112
- PMCID: PMC4493941
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1600-7
Second generation physical and linkage maps of yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) and comparison of synteny with four model fish
Abstract
Background: Physical and linkage maps are important aids for the assembly of genome sequences, comparative analyses of synteny, and to search for candidate genes by quantitative trait locus analysis. Yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata, is an economically important species in Japanese aquaculture, and genetic information will be useful for DNA-assisted breeding. We report the construction of a second generation radiation hybrid map, its synteny analysis, and a second generation linkage map containing SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) in yellowtail.
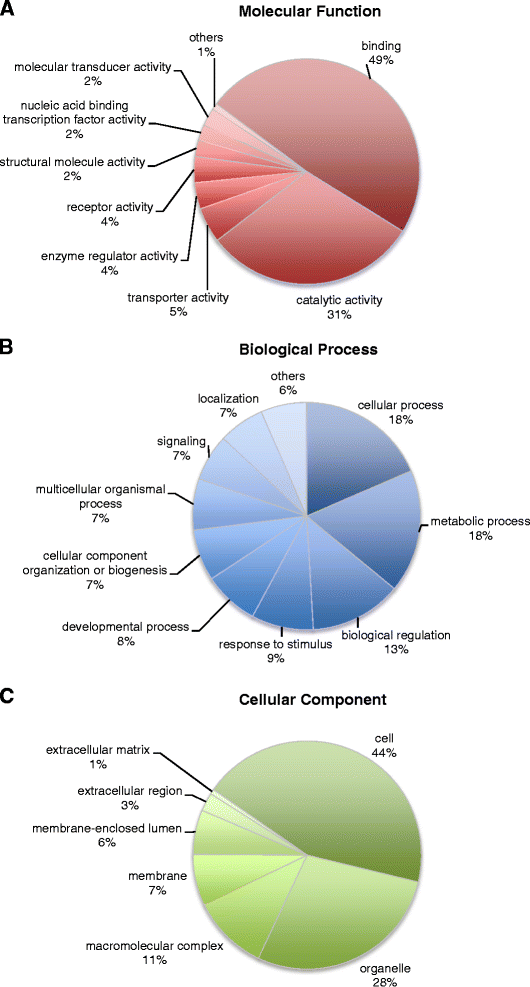
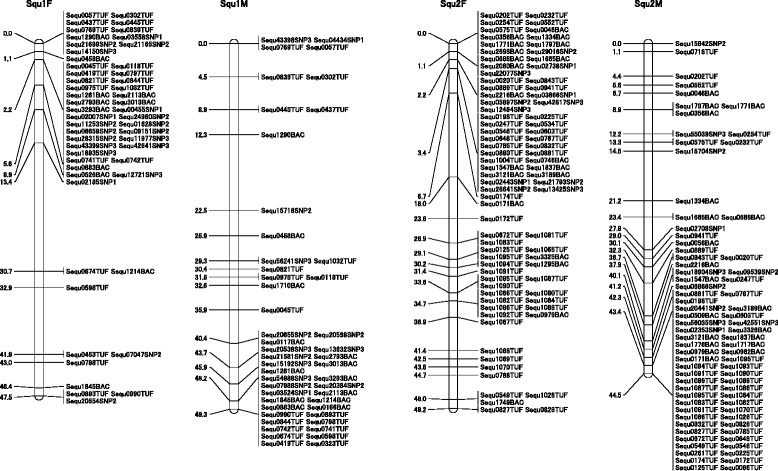
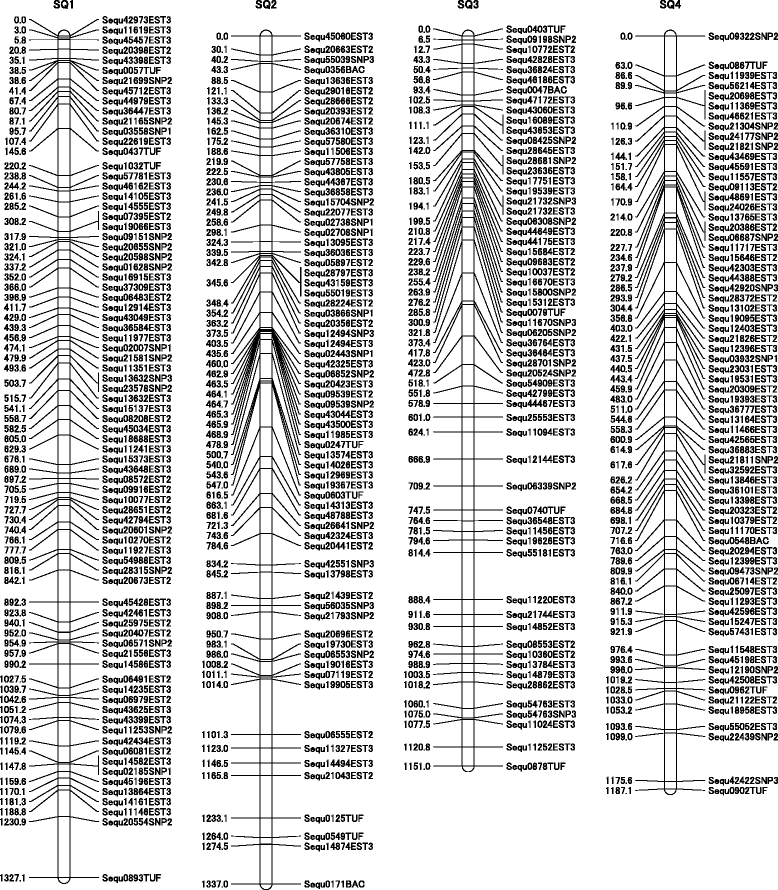
Results: Approximately 1.4 million reads were obtained from transcriptome sequence analysis derived from 11 tissues of one individual. To identify SNPs, cDNA libraries were generated from a pool of 500 whole juveniles, and the gills and kidneys of 100 adults. 9,356 putative SNPs were detected in 6,025 contigs, with a minor allele frequency ≥ 25%. The linkage and radiation hybrid maps were constructed based on these contig sequences. 2,081 markers, including 601 SNPs markers, were mapped onto the linkage map, and 1,532 markers were mapped in the radiation hybrid map.
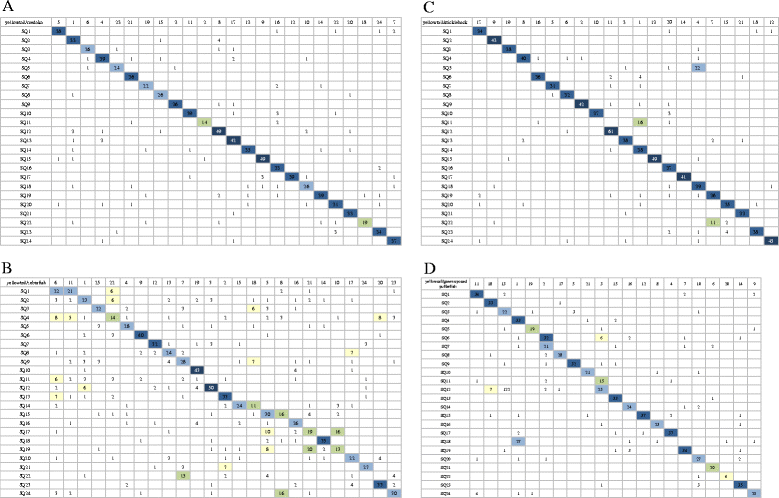
Conclusions: The second generation linkage and physical maps were constructed using 6,025 contigs having SNP markers. These maps will aid the de novo assembly of sequencing reads, linkage studies and the identification of candidate genes related to important traits. The comparison of marker contigs in the radiation hybrid map indicated that yellowtail is evolutionarily closer to medaka than to green-spotted pufferfish, three-spined stickleback or zebrafish. The synteny analysis may aid studies of chromosomal evolution in yellowtail compared with model fish.
Figures
References
-
- Wang S, Peatman E, Abernathy J, Waldbieser G, Lindquist E, Richardson P, et al. Assembly of 500,000 inter-specific catfish expressed sequence tags and large scale gene-associated marker development for whole genome association studies. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R8. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-1-r8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

