Insulin-induced changes in skeletal muscle microvascular perfusion are dependent upon perivascular adipose tissue in women
- PMID: 26003324
- PMCID: PMC4499111
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-015-3606-8
Insulin-induced changes in skeletal muscle microvascular perfusion are dependent upon perivascular adipose tissue in women
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, partly through reduced insulin-induced microvascular vasodilation, which causes impairment of glucose delivery and uptake. We studied whether perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) controls insulin-induced vasodilation in human muscle, and whether altered properties of PVAT relate to reduced insulin-induced vasodilation in obesity.
Methods: Insulin-induced microvascular recruitment was measured using contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEU), before and during a hyperinsulinaemic-euglycaemic clamp in 15 lean and 18 obese healthy women (18-55 years). Surgical skeletal muscle biopsies were taken on a separate day to study perivascular adipocyte size in histological slices, as well as to study ex vivo insulin-induced vasoreactivity in microvessels in the absence and presence of PVAT in the pressure myograph. Statistical mediation of the relation between BMI and microvascular recruitment by PVAT was studied in a mediation model.
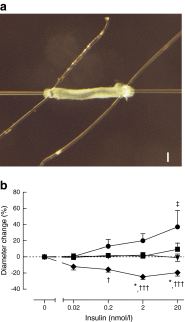
Results: Obese women showed impaired insulin-induced microvascular recruitment and lower metabolic insulin sensitivity compared with lean women. Microvascular recruitment was a mediator in the association between obesity and insulin sensitivity. Perivascular adipocyte size, determined in skeletal muscle biopsies, was larger in obese than in lean women, and statistically explained the difference in microvascular recruitment between obese and lean women. PVAT from lean women enhanced insulin-induced vasodilation in isolated skeletal muscle resistance arteries, while PVAT from obese women revealed insulin-induced vasoconstriction.
Conclusions/interpretation: PVAT from lean women enhances insulin-induced vasodilation and microvascular recruitment whereas PVAT from obese women does not. PVAT adipocyte size partly explains the difference in insulin-induced microvascular recruitment between lean and obese women.
Figures



Similar articles
-
JNK2 in myeloid cells impairs insulin's vasodilator effects in muscle during early obesity development through perivascular adipose tissue dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):H364-H374. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00663.2018. Epub 2019 May 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31149833
-
Perivascular adipose tissue control of insulin-induced vasoreactivity in muscle is impaired in db/db mice.Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):590-8. doi: 10.2337/db11-1603. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23048187 Free PMC article.
-
Lean and Obese Coronary Perivascular Adipose Tissue Impairs Vasodilation via Differential Inhibition of Vascular Smooth Muscle K+ Channels.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jun;35(6):1393-400. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305500. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25838427 Free PMC article.
-
Dual modulation of vascular function by perivascular adipose tissue and its potential correlation with adiposity/lipoatrophy-related vascular dysfunction.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(21):2185-92. doi: 10.2174/138161207781039634. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17627551 Review.
-
Paracrine regulation of vascular tone, inflammation and insulin sensitivity by perivascular adipose tissue.Vascul Pharmacol. 2012 May-Jun;56(5-6):204-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22366250 Review.
Cited by
-
Is vascular insulin resistance an early step in diet-induced whole-body insulin resistance?Nutr Diabetes. 2022 Jun 8;12(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41387-022-00209-z. Nutr Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35676248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perivascular adipose tissue: a central player in the triad of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular health.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Dec 28;23(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02549-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39732729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparisons between perivascular adipose tissue and the endothelium in their modulation of vascular tone.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3388-3397. doi: 10.1111/bph.13648. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27747871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral and intravenous glucose administration elicit opposing microvascular blood flow responses in skeletal muscle of healthy people: role of incretins.J Physiol. 2022 Apr;600(7):1667-1681. doi: 10.1113/JP282428. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35045191 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal Muscle Microvascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 13;23(2):847. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020847. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

