Myeloperoxidase formation of PAF receptor ligands induces PAF receptor-dependent kidney injury during ethanol consumption
- PMID: 26003521
- PMCID: PMC4554800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.020
Myeloperoxidase formation of PAF receptor ligands induces PAF receptor-dependent kidney injury during ethanol consumption
Abstract
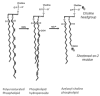
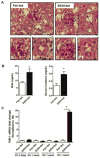
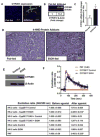
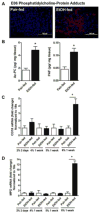
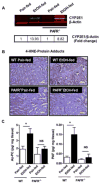
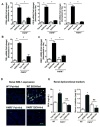
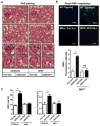
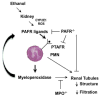
Cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) induction and oxidative metabolism of ethanol in hepatocytes inflame and damage liver. Chronic ethanol ingestion also induces kidney dysfunction, which is associated with mortality from alcoholic hepatitis. Whether the kidney is directly affected by ethanol or is secondary to liver damage is not established. We found that CYP2E1 was induced in kidney tubules of mice chronically ingesting a modified Lieber-deCarli liquid ethanol diet. Phospholipids of kidney tubules were oxidized and fragmented in ethanol-fed mice with accumulation of azelaoyl phosphatidylcholine (Az-PC), a nonbiosynthetic product formed only by oxidative truncation of polyunsaturated phosphatidylcholine. Az-PC stimulates the inflammatory PAF receptor (PTAFR) abundantly expressed by neutrophils and kidney tubules, and inflammatory cells and myeloperoxidase-containing neutrophils accumulated in the kidneys of ethanol-fed mice after significant hysteresis. Decreased kidney filtration and induction of the acute kidney injury biomarker KIM-1 in tubules temporally correlated with leukocyte infiltration. Genetic ablation of PTAFR reduced accumulation of PTAFR ligands and reduced leukocyte infiltration into kidneys. Loss of this receptor in PTAFR(-/-) mice also suppressed oxidative damage and kidney dysfunction without affecting CYP2E1 induction. Neutrophilic inflammation was responsible for ethanol-induced kidney damage, because loss of neutrophil myeloperoxidase in MPO(-/-) mice was similarly protective. We conclude that ethanol catabolism in renal tubules results in a self-perpetuating cycle of CYP2E1 induction, local PTAFR ligand formation, and neutrophil infiltration and activation that leads to myeloperoxidase-dependent oxidation and damage to kidney function. Hepatocytes do not express PTAFR, so this oxidative cycle is a local response to ethanol catabolism in the kidney.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Free radicals; Inflammation; Kidney; Oxidized phospholipids; PAF receptor; Reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory PAF Receptor Signaling Initiates Hedgehog Signaling and Kidney Fibrogenesis During Ethanol Consumption.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 31;10(12):e0145691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145691. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26720402 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol ingestion induces oxidative kidney injury through taurine-inhibitable inflammation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Apr;69:403-16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24412858 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P450 2E1 potentiates ethanol induction of hypoxia and HIF-1α in vivo.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Oct;63:175-86. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 10. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23669278 Free PMC article.
-
The discovery of the microsomal ethanol oxidizing system and its physiologic and pathologic role.Drug Metab Rev. 2004 Oct;36(3-4):511-29. doi: 10.1081/dmr-200033441. Drug Metab Rev. 2004. PMID: 15554233 Review.
-
[The role of oxidative stress in alcoholic liver injury].Med Pregl. 2009 Nov-Dec;62(11-12):547-53. doi: 10.2298/mpns0912547r. Med Pregl. 2009. PMID: 20491381 Review. Serbian.
Cited by
-
Causal effect of alcohol use on the risk of end-stage kidney disease and related comorbidities: a Mendelian randomization study.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2021 Jun;40(2):282-293. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.20.186. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34024088 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosterone-Mediated Physiological Stress Alters Liver, Kidney, and Breast Muscle Metabolomic Profiles in Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;11(11):3056. doi: 10.3390/ani11113056. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827788 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Platelet-Activating Factor Synthesis Facilitates Acute and Delayed Effects of Ethanol-Intoxicated Thermal Burn Injury.J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Nov;138(11):2461-2469. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.04.039. Epub 2018 May 30. J Invest Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29857067 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol ingestion induces glomerular filtration barrier proteins genes expression alteration and increases matrix metalloproteinases activity in the kidney of rats.Interv Med Appl Sci. 2018 Sep;10(3):171-177. doi: 10.1556/1646.10.2018.23. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2018. PMID: 30713757 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps-related genes contribute to sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.BMC Nephrol. 2025 May 14;26(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04126-y. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40369453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:307–328. - PubMed
-
- Altamirano J, Fagundes C, Dominguez M, Garcia E, Michelena J, Cardenas A, Guevara M, Pereira G, Torres-Vigil K, Arroyo V, Caballeria J, Gines P, Bataller R. Acute kidney injury is an early predictor of mortality for patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:65–71. e63. - PubMed
-
- Shankar A, Klein R, Klein BE. The association among smoking, heavy drinking, and chronic kidney disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164:263–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

