Marine Macrocyclic Imines, Pinnatoxins A and G: Structural Determinants and Functional Properties to Distinguish Neuronal α7 from Muscle α1(2)βγδ nAChRs
- PMID: 26004441
- PMCID: PMC4461042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2015.04.009
Marine Macrocyclic Imines, Pinnatoxins A and G: Structural Determinants and Functional Properties to Distinguish Neuronal α7 from Muscle α1(2)βγδ nAChRs
Abstract
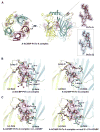
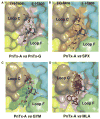
Pinnatoxins are macrocyclic imine phycotoxins associated with algal blooms and shellfish toxicity. Functional analysis of pinnatoxin A and pinnatoxin G by binding and voltage-clamp electrophysiology on membrane-embedded neuronal α7, α4β2, α3β2, and muscle-type α12βγδ nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) reveals high-affinity binding and potent antagonism for the α7 and α12βγδ subtypes. The toxins also bind to the nAChR surrogate, acetylcholine-binding protein (AChBP), with low Kd values reflecting slow dissociation. Crystal structures of pinnatoxin-AChBP complexes (1.9-2.2 Å resolution) show the multiple anchoring points of the hydrophobic portion, the cyclic imine, and the substituted bis-spiroketal and cyclohexene ring systems of the pinnatoxins that dictate tight binding between the opposing loops C and F at the receptor subunit interface, as observed for the 13-desmethyl-spirolide C and gymnodimine A congeners. Uniquely, however, the bulky bridged EF-ketal ring specific to the pinnatoxins extends radially from the interfacial-binding pocket to interact with the sequence-variable loop F and govern nAChR subtype selectivity and central neurotoxicity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
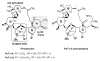

Comment in
-
From shellfish poisoning to neuroscience.Structure. 2015 Jun 2;23(6):979-80. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.05.008. Structure. 2015. PMID: 26039347
Similar articles
-
Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 30;107(13):6076-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912372107. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20224036 Free PMC article.
-
Pinnatoxins E, F and G target multiple nicotinic receptor subtypes.J Neurochem. 2015 Nov;135(3):479-91. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13245. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26173951
-
The Cyclic Imine Core Common to the Marine Macrocyclic Toxins Is Sufficient to Dictate Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonism.Mar Drugs. 2024 Mar 27;22(4):149. doi: 10.3390/md22040149. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38667766 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic imine toxins from dinoflagellates: a growing family of potent antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.J Neurochem. 2017 Aug;142 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):41-51. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13995. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28326551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic imines: chemistry and mechanism of action: a review.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Nov 21;24(11):1817-29. doi: 10.1021/tx200182m. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21739960 Review.
Cited by
-
Pinnatoxins' Deleterious Effects on Cholinergic Networks: From Experimental Models to Human Health.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 20;17(7):425. doi: 10.3390/md17070425. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31330850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Pinnatoxins A and G Reversibly Block Mouse Skeletal Neuromuscular Transmission In Vivo and In Vitro.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 24;17(5):306. doi: 10.3390/md17050306. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31137661 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Origin Ligands of Nicotinic Receptors: Low Molecular Compounds, Peptides and Proteins for Fundamental Research and Practical Applications.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 23;12(2):189. doi: 10.3390/biom12020189. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Pharmacology in 2014-2015: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, Antiviral, and Anthelmintic Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action.Mar Drugs. 2019 Dec 19;18(1):5. doi: 10.3390/md18010005. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31861527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly Selective Synthesis of Seven-Membered Azaspiro Compounds by a Rh(I)-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization/Diels-Alder Cascade of 1,5-Bisallenes.J Org Chem. 2022 Apr 15;87(8):5279-5286. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c00065. Epub 2022 Mar 24. J Org Chem. 2022. PMID: 35324177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brejc K, van Dijk WJ, Klaassen RV, Schuurmans M, van Der Oost J, Smit AB, Sixma TK. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001;411:269–276. - PubMed
-
- CCP4. The CCP4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Celie PH, van Rossum-Fikkert SE, van Dijk WJ, Brejc K, Smit AB, Sixma TK. Nicotine and carbamylcholine binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as studied in AChBP crystal structures. Neuron. 2004;41:907–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

