Mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in hypertension
- PMID: 26004493
- PMCID: PMC4609581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.05.007
Mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in hypertension
Abstract
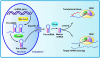
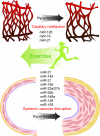
Hypertension is the major risk factor for the development of stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure and renal disease. The underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms of hypertension are complex and remain largely elusive. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, noncoding RNA fragments of 22-26 nucleotides and regulate protein expression post-transcriptionally by targeting the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA. A growing body of recent research indicates that miRNAs are important in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension. Herein, we summarize the current knowledge regarding the mechanisms of miRNAs in cardiovascular remodeling, focusing specifically on hypertension. We also review recent progress of the miRNA-based therapeutics including pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies (such as exercise training) and their potential applications in the management of hypertension.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent research progress of microRNAs in hypertension pathogenesis, with a focus on the roles of miRNAs in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):2883-2896. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4335-0. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30298350 Review.
-
microRNA-21 and hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2018 Sep;41(9):649-661. doi: 10.1038/s41440-018-0071-z. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Hypertens Res. 2018. PMID: 29973661 Review.
-
Targeting microRNAs for cardiovascular therapeutics in coronary artery disease.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014 Nov;29(6):586-94. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000107. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25159281 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in heart failure: new targets in disease management.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;94(4):480-9. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2013.138. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23852395 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Novel Players in Aortic Aneurysm.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:831641. doi: 10.1155/2015/831641. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26221607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical value of non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular, pulmonary, and muscle diseases.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):C1-C28. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00078.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31483703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acarbose attenuates migration/proliferation via targeting microRNA-143 in vascular smooth muscle cells under diabetic conditions.J Food Drug Anal. 2020 Sep 15;28(3):461-474. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.1241. J Food Drug Anal. 2020. PMID: 35696095 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Hypertension: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Hypertension. 2019 Jun;73(6):e87-e120. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000090. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 30866654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-181 in cardiovascular disease: Emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets.FASEB J. 2024 May 15;38(9):e23635. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400306R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38690685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Delivery of MicroRNA-21-3p Lowers Hypertension.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Jun 1;11:354-366. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.11.007. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 29858071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carretero OA, Oparil S. Essential hypertension. Part I: definition and etiology. Circulation. 2000;101:329–335. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, et al. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, et al. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

