Mitotic Control of Planar Cell Polarity by Polo-like Kinase 1
- PMID: 26004507
- PMCID: PMC4464975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.03.024
Mitotic Control of Planar Cell Polarity by Polo-like Kinase 1
Abstract
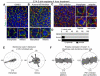
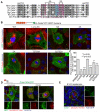
During cell division, polarized epithelial cells employ mechanisms to preserve cell polarity and tissue integrity. In dividing cells of the mammalian skin, planar cell polarity (PCP) is maintained through the bulk internalization, equal segregation, and polarized recycling of cortical PCP proteins. The dramatic redistribution of PCP proteins coincides precisely with cell-cycle progression, but the mechanisms coordinating PCP and mitosis are unknown. Here we identify Plk1 as a master regulator of PCP dynamics during mitosis. Plk1 interacts with core PCP component Celsr1 via a conserved polo-box domain (PBD)-binding motif, localizes to mitotic endosomes, and directly phosphorylates Celsr1. Plk1-dependent phosphorylation activates the endocytic motif specifically during mitosis, allowing bulk recruitment of Celsr1 into endosomes. Inhibiting Plk1 activity blocks PCP internalization and perturbs PCP asymmetry. Mimicking dileucine motif phosphorylation is sufficient to drive Celsr1 internalization during interphase. Thus, Plk1-mediated phosphorylation of Celsr1 ensures that PCP redistribution is precisely coordinated with mitotic entry.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
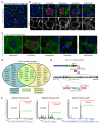
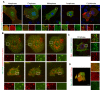
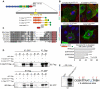
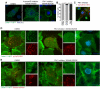

Comment in
-
Planar Pol(o)arity.Dev Cell. 2015 Jun 8;33(5):494-5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.05.022. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 26058051
References
-
- Aigouy B, Farhadifar R, Staple DB, Sagner A, Röper JC, Jülicher F, Eaton S. Cell Flow Reorients the Axis of Planar Polarity in the Wing Epithelium of Drosophila. Cell. 2010;142:773–786. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Bastock R, Strutt H, Strutt D. Strabismus is asymmetrically localised and binds to Prickle and Dishevelled during Drosophila planar polarity patterning. Development. 2003;130:3007–3014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

