Role of GDF15 (growth and differentiation factor 15) in pulmonary oxygen toxicity
- PMID: 26004619
- PMCID: PMC4553106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2015.05.008
Role of GDF15 (growth and differentiation factor 15) in pulmonary oxygen toxicity
Abstract
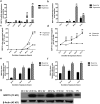
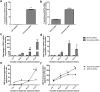
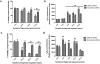
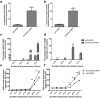
GDF15 (growth and differentiation factor 15) is a secreted cytokine, a direct target of p53 and plays a role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. It is induced by oxidative stress and has anti-apoptotic effects. The role of GDF15 in hyperoxic lung injury is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that GDF15 will be induced in vitro, in a model of pulmonary oxygen toxicity, and will play a critical role in decreasing cell death and oxidative stress. BEAS-2B (human bronchial epithelial cells) and human pulmonary vascular endothelial cells (HPMEC) were exposed to hyperoxia, and expression of GDF15 and effect of GDF15 disruption on cell viability and oxidative stress was determined. Furthermore, we studied the effect of p53 knockdown on GDF15 expression. In vitro, both BEAS-2B and HPMEC cells showed a significant increase in GDF15 expression upon exposure to hyperoxia. After GDF15 knockdown, there was a significant decrease in cell viability and increase in oxidative stress compared to control cells transfected with siRNA with a scrambled sequence. Knockdown of p53 significantly decreased the induction of GDF15 by hyperoxia. In conclusion, we show that GDF15 has a pro-survival and anti-oxidant role in hyperoxia and that p53 plays a key role in its induction.
Keywords: BEAS-2B; Bronchopulmonary dysplasia; HPMEC; Hyperoxia; Pulmonary.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Böttner M, Suter-Crazzolara C, Schober A, Unsicker K. Expression of a novel member of the TGF-beta superfamily, growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage-inhibiting cytokine-1 (GDF-15/MIC-1) in adult rat tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;297:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Clark BJ, Bull TM, Benson AB, Stream AR, Macht M, Gaydos J, Meadows C, Burnham EL, Moss M the ARDS Network Investigators. Growth differentiation factor-15 and prognosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2013;17:R92. doi: 10.1186/cc12737. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

