Drug exposure in a metastatic human lung adenocarcinoma cell line gives rise to cells with differing adhesion, proliferation, and gene expression: Implications for cancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 26004767
- PMCID: PMC4526089
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3837
Drug exposure in a metastatic human lung adenocarcinoma cell line gives rise to cells with differing adhesion, proliferation, and gene expression: Implications for cancer chemotherapy
Abstract
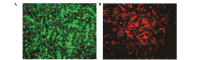
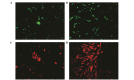
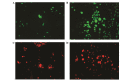
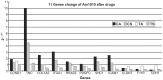
The Am1010 cell line was previously established from a metastatic deposit in an arm muscle from a patient with lung adenocarcinoma who had undergone four cycles of chemotherapy with cisplatin and taxol. Am1010 cells were labeled with red fluorescent protein or green fluorescent protein. A total of eight sublines were isolated following in vitro exposure to cisplatin or taxol. The sublines differed with regard to their adhesion and proliferation properties, with certain sublines exhibiting an increased proliferation rate and/or decreased surface adhesion. Gene expression assays demonstrated that tenascin C; cyclin D1; collagen, type 1, α2; integrin α1; related RAS viral (r‑ras) oncogene homolog 2; platelet‑derived growth factor C; and Src homolog 2 domain containing in the focal adhesion pathway, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1, F11 receptor, claudin 7 and cadherin 1 in the cell adhesion pathway, varied in expression among the sublines. The results of the present study suggested that drug exposure may alter the aggressiveness and metastatic potential of cancer cells, which has important implications for cancer chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment and characterization of a new drug surviving cell line Am1010, derived directly from muscle metastases of a human lung adenocarcinoma patient with multi-drug-resistance to cisplatin, taxol, and gefitinib.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 May;31(5):601-8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.41. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20418894 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of VBMDMP on the reversal of cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer A549/DDP cells.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jan;33(1):372-82. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3607. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25394854
-
CNTN-1 Enhances Chemoresistance in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Through Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting the PI3K/Akt Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):465-480. doi: 10.1159/000480473. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28934754
-
Increased sensitivity of human lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin associated with downregulated contactin-1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Apr;71:172-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.11.004. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25960233
-
Adhesion molecules in lung cancer: implications in the pathogenesis and management.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(22):2173-83. doi: 10.2174/138161208785740162. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18781970 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the role of exosomal microRNA-5703 in modulating tumor-associated endothelial cells in lung cancer.Cytojournal. 2024 Dec 27;21:77. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_99_2024. eCollection 2024. Cytojournal. 2024. PMID: 39917007 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-21 improves invasion and migration of drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell and transformation of EMT through targeting HBP1.Cancer Med. 2018 Jun;7(6):2485-2503. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1294. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29663730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tysnes BB, Bjerkvig R. Cancer initiation and progression: involvement of stem cells and the microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775:283–297. - PubMed
-
- Li HL, Xie SM, Zhang L, et al. Establishment and characterization of a new drug surviving cell line Am1010, derived directly from muscle metastases of a human lung adenocarcinoma patient with multi-drug-resistance to cisplatin, taxol and gefitinib. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31:601–608. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.41. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

