Molecular Consequences of the SERPINH1/HSP47 Mutation in the Dachshund Natural Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 26004778
- PMCID: PMC4505018
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.661025
Molecular Consequences of the SERPINH1/HSP47 Mutation in the Dachshund Natural Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
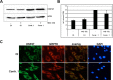
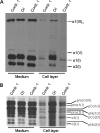
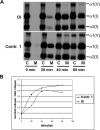
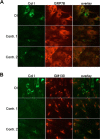
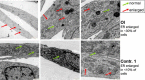
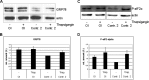
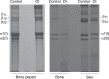
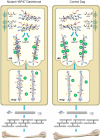
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a heritable connective tissue disease characterized by bone fragility and increased risk of fractures. Up to now, mutations in at least 18 genes have been associated with dominant and recessive forms of OI that affect the production or post-translational processing of procollagen or alter bone homeostasis. Among those, SERPINH1 encoding heat shock protein 47 (HSP47), a chaperone exclusive for collagen folding in the ER, was identified to cause a severe form of OI in dachshunds (L326P) as well as in humans (one single case with a L78P mutation). To elucidate the disease mechanism underlying OI in the dog model, we applied a range of biochemical assays to mutant and control skin fibroblasts as well as on bone samples. These experiments revealed that type I collagen synthesized by mutant cells had decreased electrophoretic mobility. Procollagen was retained intracellularly with concomitant dilation of ER cisternae and activation of the ER stress response markers GRP78 and phospho-eIF2α, thus suggesting a defect in procollagen processing. In line with the migration shift detected on SDS-PAGE of cell culture collagen, extracts of bone collagen from the OI dog showed a similar mobility shift, and on tandem mass spectrometry, the chains were post-translationally overmodified. The bone collagen had a higher content of pyridinoline than control dog bone. We conclude that the SERPINH1 mutation in this naturally occurring model of OI impairs how HSP47 acts as a chaperone in the ER. This results in abnormal post-translational modification and cross-linking of the bone collagen.
Keywords: SERPINH1; bone; collagen; connective tissue; cross-links; endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress); extracellular matrix; heat shock protein 47; osteogenesis.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant binding of mutant HSP47 affects posttranslational modification of type I collagen and leads to osteogenesis imperfecta.PLoS Genet. 2021 Feb 1;17(2):e1009339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009339. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33524049 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygosity for a missense mutation in SERPINH1, which encodes the collagen chaperone protein HSP47, results in severe recessive osteogenesis imperfecta.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Mar 12;86(3):389-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.034. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20188343 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between KDELR2 and HSP47 as a Key Determinant in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Bi-allelic Variants in KDELR2.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov 5;107(5):989-999. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 33053334 Free PMC article.
-
Bone collagen: new clues to its mineralization mechanism from recessive osteogenesis imperfecta.Calcif Tissue Int. 2013 Oct;93(4):338-47. doi: 10.1007/s00223-013-9723-9. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013. PMID: 23508630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Genetic basis for skeletal disease. Osteogenesis imperfecta and genetic abnormalities].Clin Calcium. 2010 Aug;20(8):1190-5. Clin Calcium. 2010. PMID: 20675929 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Serine protease inhibitors and human wellbeing interplay: new insights for old friends.PeerJ. 2019 Aug 30;7:e7224. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7224. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31531264 Free PMC article.
-
MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta.Nat Commun. 2016 Jul 6;7:11920. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11920. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27380894 Free PMC article.
-
HIF1 activation safeguards cortical bone formation against impaired oxidative phosphorylation.JCI Insight. 2024 Aug 1;9(18):e182330. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.182330. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39088272 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant binding of mutant HSP47 affects posttranslational modification of type I collagen and leads to osteogenesis imperfecta.PLoS Genet. 2021 Feb 1;17(2):e1009339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009339. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33524049 Free PMC article.
-
The heat shock protein 47 as a potential biomarker and a therapeutic agent in cancer research.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Dec;144(12):2319-2328. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2739-9. Epub 2018 Aug 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30128672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garbes L., Kim K., Rieß A., Hoyer-Kuhn H., Beleggia F., Bevot A., Kim M. J., Huh Y. H., Kweon H. S., Savarirayan R., Amor D., Kakadia P. M., Lindig T., Kagan K. O., Becker J., Boyadjiev S. A., Wollnik B., Semler O., Bohlander S. K., Kim J., Netzer C. (2015) Mutations in SEC24D, encoding a component of the COPII machinery, cause a syndromic form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 96, 432–439 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Engel J., Prockop D. J. (1991) The zipper-like folding of collagen triple helices and the effects of mutations that disrupt the zipper. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 20, 137–152 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

