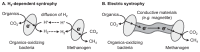Biotechnological Aspects of Microbial Extracellular Electron Transfer
- PMID: 26004795
- PMCID: PMC4462922
- DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.ME15028
Biotechnological Aspects of Microbial Extracellular Electron Transfer
Abstract
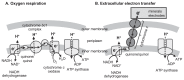
Extracellular electron transfer (EET) is a type of microbial respiration that enables electron transfer between microbial cells and extracellular solid materials, including naturally-occurring metal compounds and artificial electrodes. Microorganisms harboring EET abilities have received considerable attention for their various biotechnological applications, in addition to their contribution to global energy and material cycles. In this review, current knowledge on microbial EET and its application to diverse biotechnologies, including the bioremediation of toxic metals, recovery of useful metals, biocorrosion, and microbial electrochemical systems (microbial fuel cells and microbial electrosynthesis), were introduced. Two potential biotechnologies based on microbial EET, namely the electrochemical control of microbial metabolism and electrochemical stimulation of microbial symbiotic reactions (electric syntrophy), were also discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Aulenta F, Rossetti S, Amalfitano S, Majone M, Tandoi V. Conductive magnetite nanoparticles accelerate the microbial reductive dechlorination of trichloroethene by promoting interspecies electron transfer processes. ChemSusChem. 2013;6:433–436. - PubMed
-
- Beech IB, Sunner J. Biocorrosion: towards understanding interactions between biofilms and metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2004;15:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Bond DR, Holmes DE, Tender LM, Lovley DR. Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science. 2002;295:483–485. - PubMed
-
- Bond DR, Lovley DR. Reduction of Fe(III) oxide by methanogens in the presence and absence of extracellular quinones. Environ Microbiol. 2002;4:115–124. - PubMed