Comparison of tolerance of venlafaxine, paroxetine and amitriptyline in depression therapy
- PMID: 26005260
- PMCID: PMC4429990
- DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2015.69.107-109
Comparison of tolerance of venlafaxine, paroxetine and amitriptyline in depression therapy
Abstract
Introduction: There are no controlled studies dedicated to research of side effects of antidepressants. It is a well known fact that antidepressants reciprocally differ according to their type, intensity and frequency of appearance of certain side effects. For example, cardiovascular and anticholinergic effects are essential feature of the tricyclics whereas gastrointestinal and sexual side effects are registered during the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Interruptions of therapy or irregular use of drugs because of the appearance of side effects are not rare. Serious side effects of drugs are the fourth cause of death in the USA.
Aim: The aim of this study is the evaluation of appearance of side effects comparing three different groups of antidepressants: venlafaxine, amitriptyline and paroxetine.
Material and methods: The study included 90 in-patients as well as outpatients of both sexes aged 18-65 who were treated for major depressive disorder at Psychiatric Clinic in Banjaluka. 30 patients were treated with amitriptyline 75-250 mg, 30 patients were treated with paroxetine 20-40 mg and 30 patients were treated with venlafaxine 75-300 mg. The selection of patients was done on the basis of diagnosis of major depressive disorder.
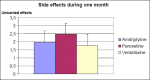
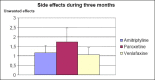
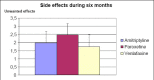
Results: Most patients did not have serious side effects. The study confirmed high efficiency of the mentioned drugs as well as the fact that paroxetine causes a bit more side effects in comparison with two other antidepressants.
Keywords: antidepressants; depression; side effects of drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet counts in depressed patients treated with amitriptyline or paroxetine.Eur Psychiatry. 2003 Mar;18(2):89-91. doi: 10.1016/s0924-9338(03)00006-3. Eur Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12711406 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of venlafaxine compared with other antidepressants and placebo in the treatment of major depression: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009 Apr;259(3):172-85. doi: 10.1007/s00406-008-0849-0. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19165525
-
[Comparative efficacy and tolerability of paroxetine and amitriptiline in long-term therapy preventing depressive recurrences].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2005;105(10):22-9. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2005. PMID: 16281375 Clinical Trial. Russian.
-
Safety and tolerability of the new antidepressants.J Clin Psychiatry. 1997;58 Suppl 6:26-31. J Clin Psychiatry. 1997. PMID: 9227670 Review.
-
Paroxetine in the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Aug;5(8):1799-806. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.8.1799. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15264994 Review.
Cited by
-
Psychotropic Drugs for the Management of Chronic Pain and Itch.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Jun 24;12(2):99. doi: 10.3390/ph12020099. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31238561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory treatment for major depressive disorder: implications for patients with an elevated immune profile and non-responders to standard antidepressant therapy.J Psychopharmacol. 2017 Sep;31(9):1149-1165. doi: 10.1177/0269881117711708. Epub 2017 Jun 27. J Psychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28653857 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lam RW, Mok H. Depression, Oxford University Press, Lundbeck Institute; 2008.
-
- Henriksson S, Asplund R, Boethius G, Hällström T, Isacsson G. Infrequent use of antidepressants in depressed individuals (an interview and prescription database study in a defined Swedish population 2001-2002. Eur Psychiatry. 2006;21:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Lisulov R, Nedić A. Novi Sad: University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Medicine; 2006. Problems of diagnostics and treatment of depressive disorders in primary care institutions in Autonomous Region Vojvodina.
-
- Kenedi SH, Lam RW, Cohen NL, Ravindran AV. Clinical guidelines for the treatment of depressive disorders. IV. Medications and other biological treatments. Can J Psychiatry. 200;46:38–58. - PubMed
-
- Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA. 1998;279:1200–1205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources