Lentiviral Vectors Mediate Long-Term and High Efficiency Transgene Expression in HEK 293T cells
- PMID: 26005375
- PMCID: PMC4441065
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.11270
Lentiviral Vectors Mediate Long-Term and High Efficiency Transgene Expression in HEK 293T cells
Abstract
Objectives: Lentiviral vectors have been used successfully to rapidly produce decigram quantities of active recombinant proteins in mammalian cell lines. To optimize the protein production platform, the roles of Ubiquitous Chromatin Opening Element (UCOE), an insulator, and selected promoters were evaluated based on efficiency and stability of foreign gene expression mediated by lentiviral vectors.
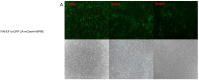
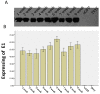
Methods: Five lentiviral vectors, pFIN-EF1α-GFP-2A-mCherH-WPRE containing EF1α promoter and HS4 insulator, p'HR.cppt.3'1.2kb-UCOE-SFFV-eGFP containing SFFV promoter and UCOE, pTYF-CMV(β-globin intron)-eGFP containing CMV promoter and β-globin intron, pTYF-CMV-eGFP containing CMV promoter, and pTYF-EF1α-eGFP with EF1α promoter were packaged, titered, and then transduced into 293T cells (1000 viral genomes per cell). The transduced cells were passaged once every three days at a ratio of 1:10. Expression level and stability of the foreign gene, green fluorescence protein (GFP), was evaluated using fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry. Furthermore, we constructed a hepatitis C virus (HCV) E1 recombinant lentiviral vector, pLV-CMV-E1, driven by the CMV promoter. This vector was packaged and transduced into 293T cells, and the recombinant cell lines with stable expression of E1 protein were established by limiting dilution.
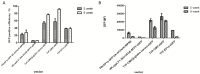
Results: GFP expression in 293T cells transduced with the five lentiviral vectors peaked between passages 3 and 5 and persisted for more than 5 weeks. The expression was prolonged in the cells transduced with TYF-CMV (β-globin intron)-eGFP or TYF-CMV-eGFP, demonstrating less than a 50% decrease even at 9 weeks post transduction (p>0.05). The TYF-CMV-eGFP-transduced cells began with a higher level of GFP expression than other vectors did. The percentage of GFP positive cells for any of the five lentiviral vectors sustained over time. Moreover, the survival rates of all transfected cells exceeded 80% at both 5 and 9 weeks post transduction. Surprisingly, neither the HS4 insulator nor the UCOE sequence improved the GFP expression level or stability. Clonal cell lines with HCV E1 gene were generated from LV-CMV-E1 vector-infected 293T cells. A representative recombinant cell line maintained stable E1expression for at least 9 weeks without significant difference in morphology compared with untreated 293T cells.
Conclusion: The results suggest that all five vectors can stably transduce 293T cells, producing long term transgene expression with different efficiencies. However, neither the insulator nor the UCOE improved the GFP expression. The vectors containing the promoter CMV or CMV (β-globin intron) generated the highest gene expressions, manifesting as more favorable candidates for recombinant protein production in HEK293T cells.
Keywords: HCV E1.; HEK 293 cells; UCOE; insulator; lentiviral vector; promoters; protein production.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Construction of a recombinant lentiviral vector of p38 MAPK and establishment of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line stably expressing p38 MAPK].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Mar;32(3):317-21. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22445974 Chinese.
-
Lentivirus vector driven by polybiquitin C promoter without woodchuck posttranscriptional regulatory element and central polypurine tract generates low level and short-lived reporter gene expression.Gene. 2012 May 1;498(2):231-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.071. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Gene. 2012. PMID: 22366305
-
Transient Expression of Green Fluorescent Protein in Integrase-Defective Lentiviral Vector-Transduced 293T Cell Line.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1448:159-73. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3753-0_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27317180
-
Strategies for targeting lentiviral vectors.Curr Gene Ther. 2008 Dec;8(6):449-60. doi: 10.2174/156652308786848003. Curr Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 19075628 Review.
-
Toward Tightly Tuned Gene Expression Following Lentiviral Vector Transduction.Viruses. 2020 Dec 11;12(12):1427. doi: 10.3390/v12121427. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33322556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and Antigenicity of the Ectodomain of Rabies Virus Glycoprotein Stably Expressed in HEK293T Cells.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Aug 15;20(10):1282-1292. doi: 10.7150/ijms.87134. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37786447 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of a stable HEK293T cell line with c.392G>T (p.131G>V) mutation site knockout in G6PD gene using CRISPR/Cas9 technique].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Mar 30;39(3):320-327. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.03.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31068316 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Visualizing Angiogenesis by Multiphoton Microscopy In Vivo in Genetically Modified 3D-PLGA/nHAp Scaffold for Calvarial Critical Bone Defect Repair.J Vis Exp. 2017 Sep 7;(127):55381. doi: 10.3791/55381. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28930985 Free PMC article.
-
The Accurate and Exclusive Quantification of Somatic Cells in Raw Milk with an OPD-Cu2+ System-Based Colorimetric Method.Foods. 2024 Sep 12;13(18):2890. doi: 10.3390/foods13182890. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39335819 Free PMC article.
-
miR-129-5p Inhibits Adipogenesis through Autophagy and May Be a Potential Biomarker for Obesity.Int J Endocrinol. 2019 Nov 6;2019:5069578. doi: 10.1155/2019/5069578. eCollection 2019. Int J Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31781210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hannig G, Makrides SC. Strategies for optimizing heterologous protein expression in Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16(2):54–60. - PubMed
-
- Baneyx F, Mujacic M. Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nature biotechnology. 2004;22(11):1399–1408. - PubMed
-
- Daly R, Hearn MT. Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: a useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production. Journal of molecular recognition: JMR. 2005;18(2):119–138. - PubMed
-
- Caterina Holz, Bianka Prinz, Natalia Bolotina, Volker Sievert, Konrad Büssow, Bernd Simon, Ulf Stahl, Lang C. Establishing the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a system for expression of human proteins on a proteome-scale. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2003;4(2-3):97–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

