Elevated Serum Leptin Level Is Associated with Body Mass Index But Not with Serum C-reactive Protein and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate Values in Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 26005385
- PMCID: PMC4404954
- DOI: 10.5455/msm.2015.27.99-103
Elevated Serum Leptin Level Is Associated with Body Mass Index But Not with Serum C-reactive Protein and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate Values in Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
Objectives: Aim of the present study was to investigate serum concentration of leptin and its association with values of body mass index (BMI), C-reactive protein (CRP), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in hemodialysis (HD) patients.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 60 HD patients (34 male, 26 female) and 30 age- and sex-matched (4 males, 26 females) apparently healthy subjects. Serum leptin concentration was determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Serum CRP concentration was measured by means of particle-enhanced immunonephelometry. ESR value was determined by Western Green method. BMI was calculated as weight (kg) divided by height squared (m(2)).
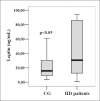
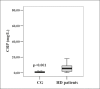
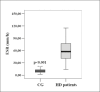
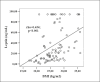
Results: Results have shown that median serum leptin concentration (30.65 ng/mL; 12.48-86.40 ng/mL) was statistically significantly higher in HD patients compared to median serum leptin concentration (15.75 ng/mL; 9.15-30.65 ng/mL) in the control group of healthy subjects (p<0.05). Likewise, median serum CRP concentration (5.5 mg/L; 1.93-8.9 mg/L) and median ESR value (57.5 mm/h; 40.5-77.0 mm/h) were significantly higher in HD patients compared to median serum CRP concentration (0.8 mg/L; 0.38-1.43 mg/L) (p<0.001) and median ESR value (10.0 mm/h; 6.5-14.0 mm/h) (p<0.001) determined in the control group. Statistically significant positive correlation was found between BMI values and serum leptin concentration in HD patients (rho=0.434; p<0.001). Positive, although not significant, correlation was observed between serum CRP and leptin levels in HD patients (rho=0.171; p>0.05). Negative correlation between ESR values and serum leptin concentrations in HD patients was determined but it was not statistically significant (rho= -0.029; p>0.05).
Conclusions: Increased serum concentration of leptin as pro-inflammatory cytokine as well as elevated serum values of CRP and ESR indicate presence of systemic micro inflammation in HD patients. Results of the present study point to possible use of serum leptin concentration as an indicator of nutritional status in HD patients based on observed significant positive correlation between serum leptin concentrations and BMI values. However, absence of significant association between serum leptin and CRP levels as well as between serum leptin concentrations and ESR values in HD patients requires further investigation and clarification.
Keywords: Body Mass Index (BMI); C-reactive protein (CRP); Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR); Hemodialysis (HD) patients; Leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Procaccini C, Jirillo E, Matarese G. Leptin as an immunomodulator. Mol Aspects Med. 2012;33(1):35–45. - PubMed
-
- Soltani Z, Washco V, Morse S, Reisin E. The impacts of obesity on the cardiovascular and renal systems: cascade of events and therapeutic approaches. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015;17(2):520. - PubMed
-
- Carbone F, La Rocca C, Matarese G. Immunological functions of leptin and adiponectin. Biochimie. 2012;94(10):2082–2088. - PubMed
-
- de Lima SM, Otoni A, Sabino Ade P, Dusse LM, Gomes KB, Pinto SW, Marinho MA, Rios DR. Inflammation, neoangiogenesis and fibrosis in peritoneal dialysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;421:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Lech M, Rommele C, Anders HJ. Pentraxins in nephrology: C-reactive protein, serum amyloid P and pentraxin-3. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(4):803–811. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
