Evaluating Reliability and Predictive Validity of the Persian Translation of Quantitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (Q-CHAT)
- PMID: 26005483
- PMCID: PMC4434431
Evaluating Reliability and Predictive Validity of the Persian Translation of Quantitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (Q-CHAT)
Abstract
Objective: Early screening of autism increases the chance of receiving timely intervention. Using the Parent Report Questionnaires is effective in screening autism. The Q-CHAT is a new instrument that has shown several advantages than other screening tools. Because there is no adequate tool for the early screening of autistic traits in Iranian children, we aimed to investigate the adequacy of the Persian translation of Q-CHAT.
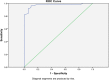
Method: At first, we prepared the Persian translation of the Quantitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (Q-CHAT). After that, an appropriate sample was selected and the check list was administered. Our sample included 100 children in two groups (typically developing and autistic children) who had been selected conveniently. Pearson's r was used to determine test-retest reliability, and Cronbach's alpha coefficient was used to explore the internal consistency of Q-CHAT. We used the receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC) to investigate whether Q-CHAT can adequately discriminate between typically developing and ASD children or not. Data analysis was carried out by SPSS 19.
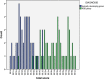
Result: The typically developing group consisted of 50 children with the mean age of 27.14 months, and the ASD group included50 children with the mean age of 29.62 months. The mean of the total score for the typically developing group was 22.4 (SD=6.26) on Q-CHAT and it was 50.94 (SD=12.35) for the ASD group, which was significantly different (p=0.00).The Cronbach's alpha coefficient of the checklist was 0.886, and test-retest reliability was calculated as 0.997 (p<0.01). The estimated area under the curve (AUC) was 0.971. It seems that the total score equal to 30 can be a good cut point to identify toddlers who are at risk of autism (sensitivity= 0.96 and specificity= 0.90).
Conclusion: The Persian translation of Q-CHAT has good reliability and predictive validity and can be used as a screening tool to detect 18 to 24 months old children who are at risk of autism.
Keywords: Autism; Early Screening; Predictive Validity; Q-CHAT; Reliability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and Validity of the Korean Translation of Quantitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers: A Preliminary Study.Soa Chongsonyon Chongsin Uihak. 2018 Apr 1;29(2):80-85. doi: 10.5765/jkacap.2018.29.2.80. Soa Chongsonyon Chongsin Uihak. 2018. PMID: 32595299 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Quantitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers in an Italian Clinical Sample of Young Children With Autism and Other Developmental Disorders.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Jul 17;10:488. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00488. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31427993 Free PMC article.
-
A modified screening tool for autism (Checklist for Autism in Toddlers [CHAT-23]) for Chinese children.Pediatrics. 2004 Aug;114(2):e166-76. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e166. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15286253
-
Early identification of autism: a comparison of the Checklist for Autism in Toddlers and the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers.J Paediatr Child Health. 2013 Jun;49(6):438-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2012.02558.x. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Paediatr Child Health. 2013. PMID: 22971004 Review.
-
Screening for autism in young children: The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) and other measures.Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2005;11(3):253-62. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20072. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 16161090 Review.
Cited by
-
Culturally adapted pictorial screening tool for autism spectrum disorder: A new approach.World J Clin Pediatr. 2017 Feb 8;6(1):45-51. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v6.i1.45. eCollection 2017 Feb 8. World J Clin Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28224095 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review: cultural adaptation and feasibility of screening for autism in non-English speaking countries.Int J Ment Health Syst. 2018 May 8;12:22. doi: 10.1186/s13033-018-0200-8. eCollection 2018. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2018. PMID: 29760771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing a Comprehensive Evidence-Based Service Package for Toddlers with Autism in a Low Resource Setting: Early Detection, Early Intervention, and Care Coordination.Iran J Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;14(2):120-129. Iran J Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31440293 Free PMC article.
-
Testing an online screening for autism in the COVID-19 pandemic: a psychometric study of the Q-CHAT-24 in Chilean toddlers.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 17;15:1363976. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1363976. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38952633 Free PMC article.
-
Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorders Measured by the Qualitative Checklist for Autism in Toddlers in a Large Sample of Polish Toddlers.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 5;19(5):3072. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19053072. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35270764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association., American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5 Task Force. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-5. 5th. City: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Harris SL, Handleman JS. Age and IQ at intake as predictors of placement for young children with autism: a four- to six-year follow-up. Journal of autism and developmental disorders 2000; 30: 137–142. - PubMed
-
- Dababnah S, Parish SL, Turner Brown L, Hooper SR. Early screening for autism spectrum disorders: A primer for social work practice. Children and Youth Services Review 2011; 33: 265–273.
-
- Daniels AM, Mandell DS. Children’s Compliance with American Academy of Pediatrics’ Well-Child Care Visit Guidelines and the Early Detection of Autism. Journal of autism and developmental disorders 2013; 43: 2844–2854. - PubMed
-
- National Research Council (U.S.). Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism. Educating children with autism. City: National Academy Press; 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources