Discovery of Quinazoline-Based Fluorescent Probes to α1-Adrenergic Receptors
- PMID: 26005522
- PMCID: PMC4434465
- DOI: 10.1021/ml5004298
Discovery of Quinazoline-Based Fluorescent Probes to α1-Adrenergic Receptors
Abstract
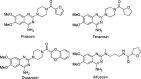
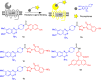
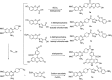
α1-Adrenergic receptors (α1-ARs), as the essential members of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), can mediate numerous physiological responses in the sympathetic nervous system. In the current research, a series of quinazoline-based small-molecule fluorescent probes to α1-ARs (1a-1e), including two parts, a pharmacophore for α1-AR recognition and a fluorophore for visualization, were well designed and synthesized. The biological evaluation results displayed that these probes held reasonable fluorescent properties, high affinity, accepted cell toxicity, and excellent subcellular localization imaging potential for α1-ARs.
Keywords: cell imaging; fluorescent probes; quinazoline; subcellular localization; α1-Adrenergic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
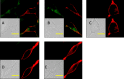
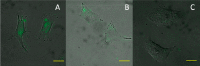
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of naphthalimide-based fluorescent probes for α1-adrenergic receptors.Drug Discov Ther. 2014 Feb;8(1):11-7. doi: 10.5582/ddt.8.11. Drug Discov Ther. 2014. PMID: 24647153
-
Discovery of Environment-Sensitive Fluorescent Agonists for α1-Adrenergic Receptors.Anal Chem. 2019 Oct 1;91(19):12173-12180. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01059. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31321979
-
Photoinduced Electron Transfer-Based Fluorescent Agonists for α1-Adrenergic Receptors Imaging.Anal Chem. 2021 Apr 20;93(15):6034-6042. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03841. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33830731
-
α1-Adrenergic receptor subtypes in the central nervous system: insights from genetically engineered mouse models.Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(6):1489-97. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71509-3. Pharmacol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24552996 Review.
-
Clinical implications from studies of alpha1 adrenergic receptor knockout mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Apr 15;73(8):1107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17141736 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Fluorescence Polarization Probe for the ELISA-Based Antagonist Screening of α1-Adrenergic Receptors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Aug 26;7(10):967-971. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00048. eCollection 2016 Oct 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27774138 Free PMC article.
-
First small-molecule PROTACs for G protein-coupled receptors: inducing α 1A-adrenergic receptor degradation.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Sep;10(9):1669-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.014. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33088687 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-permeable probe for the labelling of a bacterial glycosyltransferase and virulence factor.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 Oct 19;5(1):55-62. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00092c. eCollection 2024 Jan 3. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 38179196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li W.; Du L.; Li M. Alkaloids and flavonoids as α1-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4923–4932. - PubMed
-
- Ruffolo R. R. Jr; Hieble J. P. Adrenoceptor pharmacology: urogenital applications. Eur. Urol. 1999, 36, 17–22. - PubMed
-
- Forray C.; Noble S. A. Subtype selective α1-adrenoceptor antagonists for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Expert Opin. Invest. Drug. 1999, 8, 2073–2094. - PubMed
-
- Nagarathnam D.; Wetzel J.; Miao S.; Marzabadi M.; Chiu G.; Wong W.; Hong X.; Fang J.; Forray C.; Branchek T. Design and synthesis of novel α1a adrenoceptor-selective dihydropyridine antagonists for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 5320–5333. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

